Geomembrane is a high-performance polymer barrier used for seepage control, containment, and environmental protection across landfills, mining, water reservoirs, canals, tailings, aquaculture, and agriculture.
Our ISO-verified quality, high chemical and puncture resistance, UV stability, and long service life—engineered for consistent weldability and fast field installation. With advanced extrusion lines and strict QC (thickness, carbon black, OIT, tensile/tear), your projects run on reliable materials and predictable performance.
Discover Our Best Geomembrane Collection
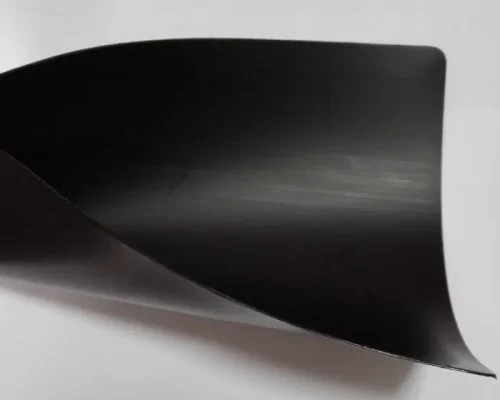

HDPE Geomembrane
Manufactured from virgin HDPE with UV/antioxidant packages, this liner delivers outstanding chemical resistance, stress-crack resistance, and long-term durability. Available smooth or textured (single/double) to optimize interface friction, it welds cleanly by hot wedge/extrusion for rapid, secure seams. From our ISO-certified plant, you receive uniform thickness and roll width, stable resin grades, and full QC documentation—your proven choice for landfill base liners, heap-leach pads, ponds, and canals.
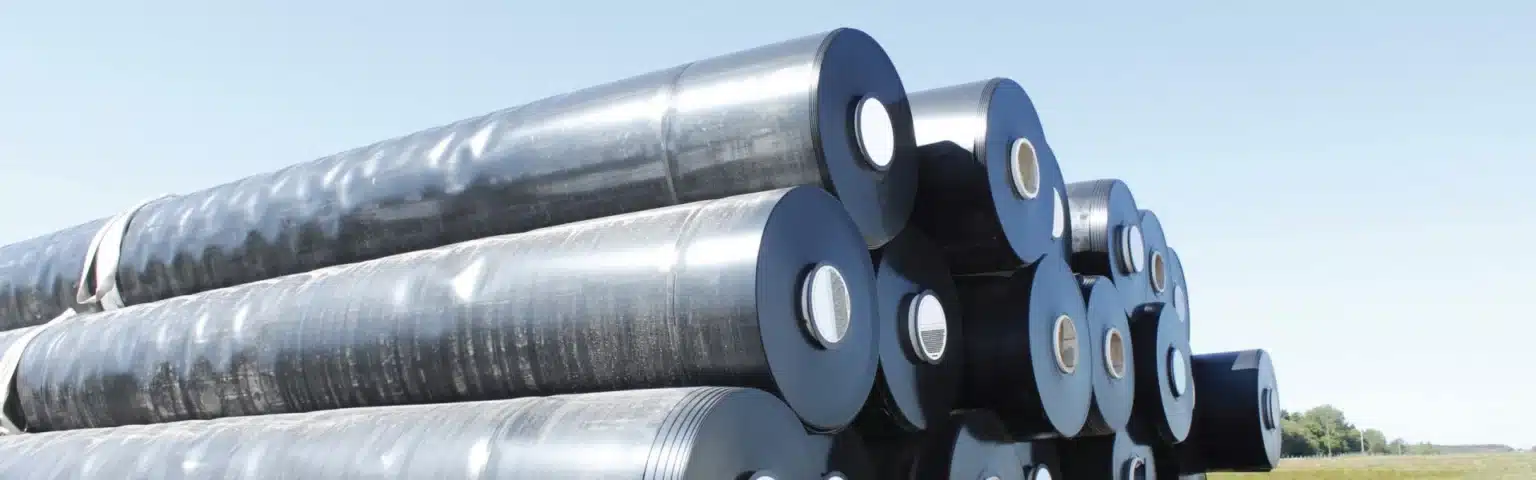

Types of Geomembrane
We offer a full portfolio of geomembrane liners to match your project and procurement needs. From resin grade and thickness to surface finish, color, and roll format, each option is engineered for reliable containment, fast installation, and long service life. Explore the ranges below and select the liner configuration that fits your specifications.
By Materials

HDPE Geomembrane
Produced from high-density polyethylene with UV and antioxidant packages, this liner offers excellent chemical resistance, stress-crack resistance, and durability. It’s the go-to choice for landfills, heap leach pads, ponds, canals, and reservoirs where long-term performance and weldability are critical.
Composite Geomembrane
A factory-bonded laminate combining a polymer liner with nonwoven geotextile to enhance puncture resistance, cushioning, and slope friction. Ideal over irregular subgrades or side slopes, helping reduce underliner demands while improving survivability and handling.
By Surface Geomembrane

Smooth Geomembrane
Flat surfaces deliver efficient factory QC, rapid field deployment, and high seam productivity with hot-wedge/extrusion welding. Best where interface friction is less critical—such as pond bases, cells with ballast, or areas receiving protective layers.

Textured Geomembrane
Engineered texture increases interface friction for side slopes, capped cells, and lining systems requiring shear stability. Single- or double-sided texture options allow you to tailor friction values without sacrificing seam quality.
By Thickness Class

Standard Duty (0.5–1.0 mm)
Lightweight sheets for canals, aquaculture, decorative ponds, and secondary containment where rapid placement and conformance are priorities. Lower material mass aids handling and detailing around penetrations.

Heavy Duty (1.5–3.0 mm)
Thicker gauges for landfills, mining, and high-load containment require superior puncture resistance and extended service life. Increased rigidity supports consistent seam profiles and reduces the risk of damage during cover placement.
By Color & Thermal Control

Black Geomembrane
Black (Carbon-Black Stabilized), industry standard for UV protection and long-term outdoor exposure. High opacity minimizes photodegradation and provides a uniform appearance across large cells.

White / Green Geomembrane
Light-colored surfaces improve visual inspection, reduce surface temperature in hot climates, and support worker safety. Common on exposed caps, tanks, and sites with thermal-management requirements.
Geomembrane Applications

Geomembrane for Aquaculture
Used for fish, shrimp, and crab ponds, geomembrane liners prevent seepage and maintain clean water. They ensure higher productivity and long-term waterproofing. Applications: Fish pond, tilapia pond, shrimp pond, crab pond, aquaculture liner.

Geomembrane for Landfill
Geomembranes protect soil and groundwater by isolating waste and preventing leachate leakage. Ideal for modern waste management and treatment systems. Applications: Landfill liner, sewage treatment, hazardous waste, industrial waste.

Geomembrane for Dam and Irrigation
Perfect for reservoirs and canals, geomembranes reduce water loss and strengthen infrastructure for efficient water storage and distribution. Applications: Dam liner, canal liner, water reservoir, irrigation pond.

Geomembrane for Mining Projects
In mining, geomembranes act as durable barriers for heap leaching and tailings, protecting soil and groundwater from chemical contamination. Applications: Heap leach pad, tailing pond, settling basin, solution pond.

Geomembrane for Oil & Gas Projects
Geomembranes provide secure containment for fluids and chemicals in oil and gas operations, ensuring safety and environmental compliance. Applications: Freshwater pond, flowback pond, well pad, pit liner, containment area.
Geomembrane Price(Geomembrane Liner Cost)
The price of geomembranes is not fixed and depends primarily on the following factors:
Raw Material – 100% virgin HDPE costs more but offers the best strength and durability.
Thickness – The thicker the geomembrane (0.3mm–2.0mm), the higher the price.
Surface Type – Textured geomembranes are slightly more expensive than smooth ones.
Order Quantity – Bulk and wholesale orders reduce the unit cost.
Project Application – Demanding projects like landfills or mining require premium-grade material.

Excell Geomembrane Manufacturer Production
1️⃣ Raw Material Preparation – HDPE resin is carefully dried and formulated for stable extrusion.
2️⃣ Melting & Extrusion – Resin is melted in the extruder and pushed through a screw system for shaping.
3️⃣ Film Formation – Molten resin passes through a circular die to form a continuous tubular film.
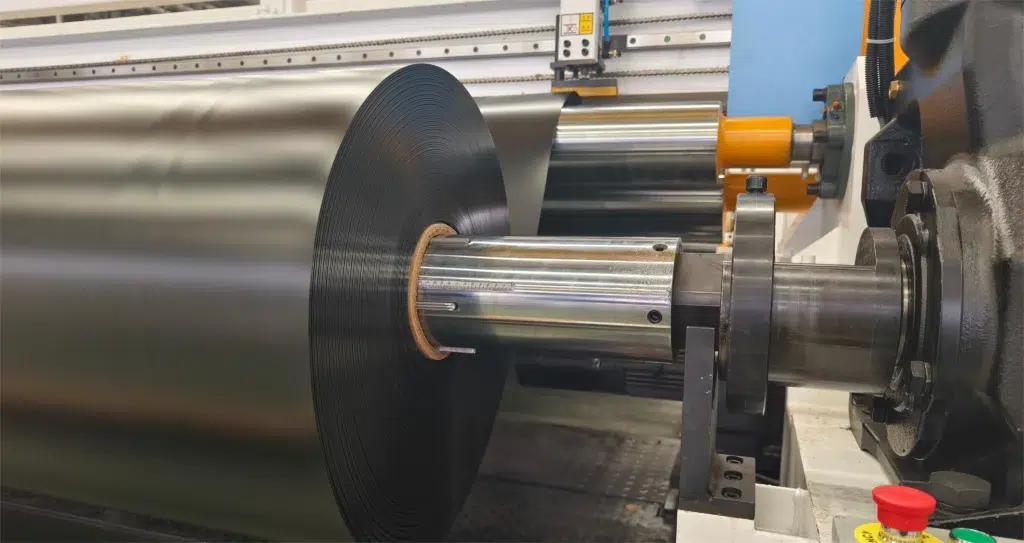
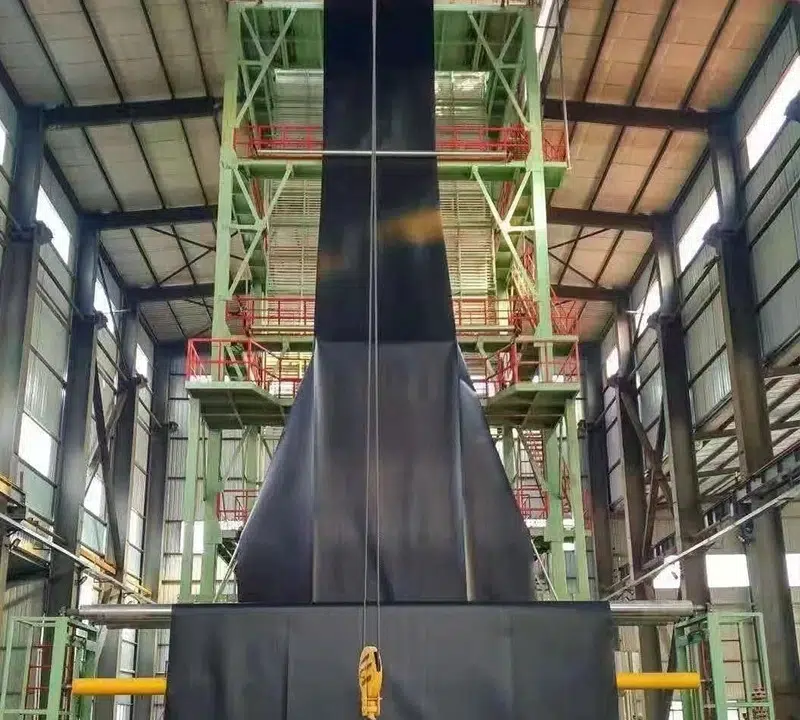


4️⃣ Expansion & Cooling – Air pressure expands the tube evenly; it is then cooled rapidly with air or water.
5️⃣ Trimming & Flattening – The film edges are cut smoothly, flattened, and shaped for precise dimensions.
6️⃣ Winding & Packaging – Finished geomembrane sheets are wound into rolls for transport and installation.
Completed Projects
Countries/areas served
Employees
Years In Business
Client Testimonials
Our clients love us, here are a few of their quotes.
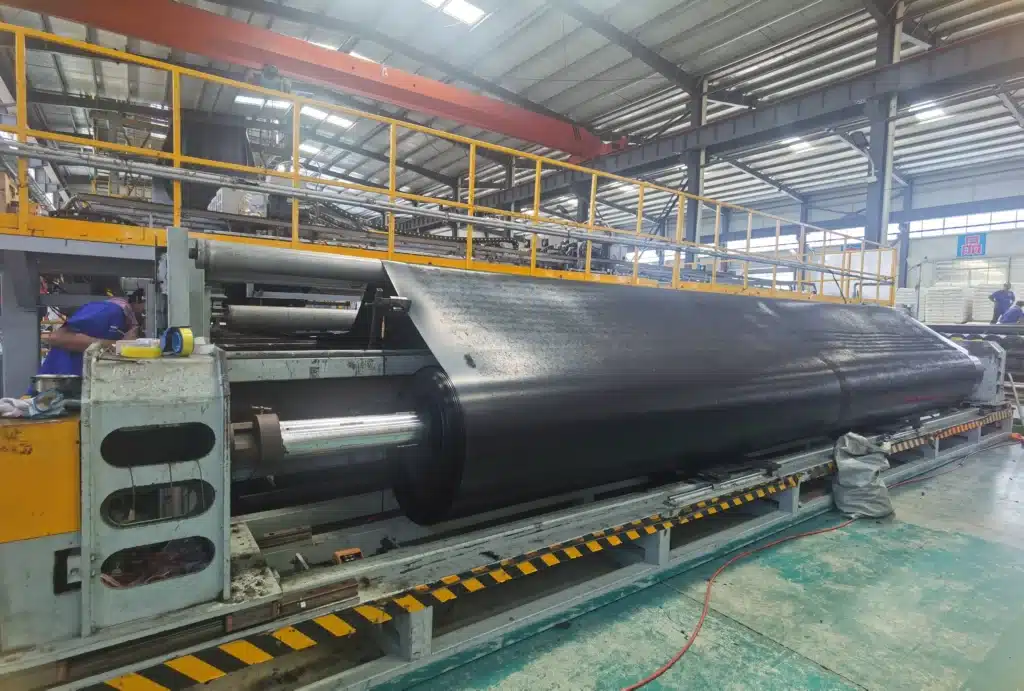





Which Geomembrane is right for your Project?
Our expert team helps you choose the right geomembrane for your project’s structural, environmental, and financial needs. Whether it’s HDPE geomembrane (geomembrana HDPE) for landfill lining, flexible LLDPE liners, or custom solutions, we deliver reliable recommendations.
As a trusted geomembrane manufacturer and supplier, MJY provides high-performance liners known for durability, chemical resistance, and environmental protection. Recognized as a geomembrane best manufacturer, we serve global markets with solutions built for efficiency and sustainability.


FAQ
What are the Disadvantages of Geomembrane?
While geomembranes (including HDPE geomembrana) are widely used for landfill lining, ponds, mining, and wastewater treatment due to their impermeability and durability, there are some disadvantages to consider:
- Installation Challenges – Geomembranes require skilled installation. Improper welding or surface preparation can lead to leaks.
- Puncture Risk – Sharp objects, roots, or heavy equipment can puncture or damage the liner if not properly protected.
- UV Sensitivity – Long-term exposure to sunlight may degrade certain geomembrane types without protective cover.
- Temperature Limitations – Extreme cold or high heat can affect flexibility and long-term performance.
- Cost of Repairs – Detecting and repairing leaks can be complex and expensive.
Despite these limitations, when installed and maintained correctly, geomembranes remain one of the most effective and cost-efficient solutions for containment and environmental protection.
How Long Do Geomembranes Last?
The lifespan of a geomembrane liner depends on the material, installation, and exposure conditions. HDPE geomembrana can last 20–30 years or more when properly installed and covered, making it a reliable solution for large-scale environmental and infrastructure projects.
What Are the Advantages of Using Geomembranes?
Geomembranes provide superior impermeability, chemical resistance, and durability compared to traditional liners. They are cost-effective, easy to transport, and suitable for diverse applications, from landfill containment to aquaculture ponds.
What Types of Geomembranes Are Available?
There are several types of geomembranes, including HDPE geomembrane, LDPE geomembrane, PVC geomembrane, and EPDM liners. Among them, HDPE geomembrana is the most widely used due to its high chemical resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
How Thick Should a Geomembrane Be?
The thickness of a geomembrane liner depends on its application. Common thicknesses range from 0.5 mm to 3 mm. For example, landfills and mining projects usually require thicker geomembranes for maximum durability, while ponds and aquaculture can use thinner liners.
Is Geomembrane Installation Difficult?
Yes, geomembrane installation requires trained professionals and specialized equipment. Proper seaming, welding, and quality control are critical to ensure impermeability and prevent leakage. Working with an experienced geomembrane manufacturer and supplier helps guarantee reliable results.
MJY is a trusted geosynthetic manufacturer for over 10 years with our expertise and vast knowledge in the industry.
