How to install grass grids?
I see many buyers want green parking that can carry cars. You worry about rutting, mud, and failed trials. You also want a clear, repeatable build.
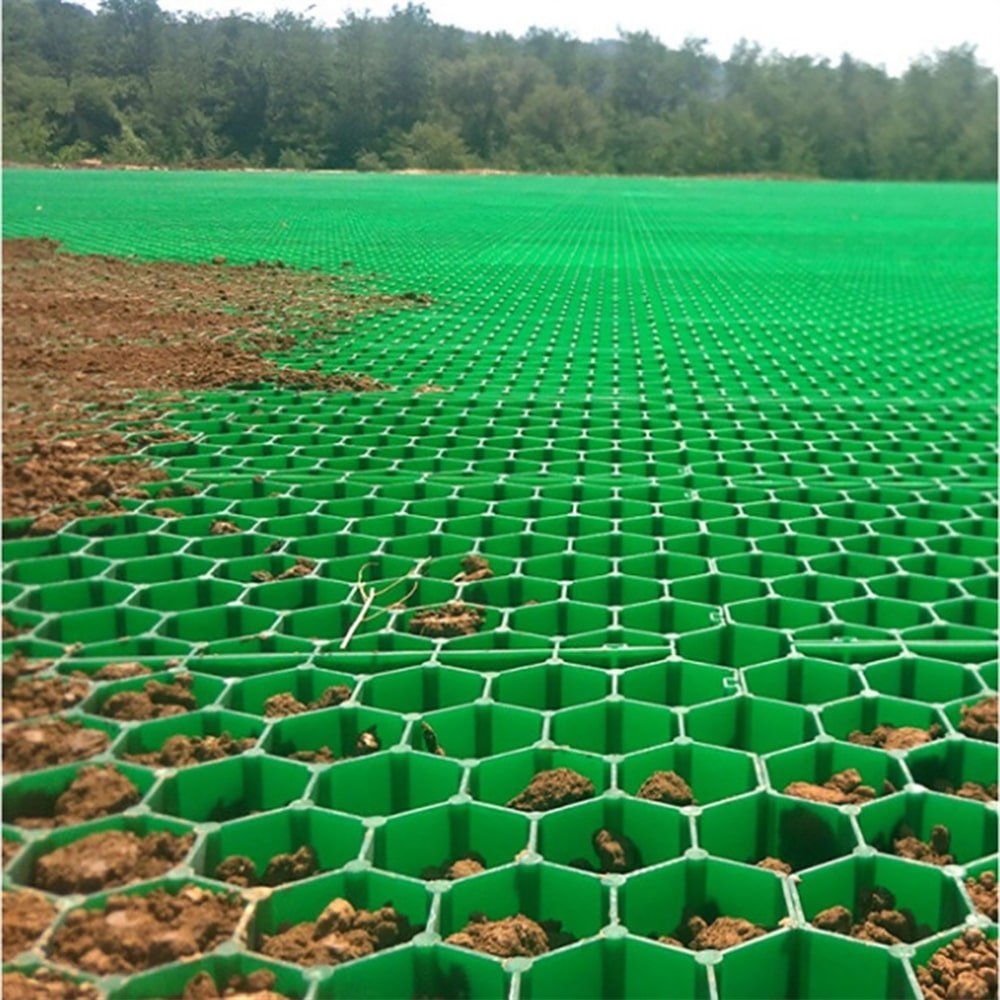
Grass grids install like a light-duty pavement. I prepare the base, add geotextile, place and lock panels, fill cells with soil-sand, then seed or turf. The result carries traffic and stays green.
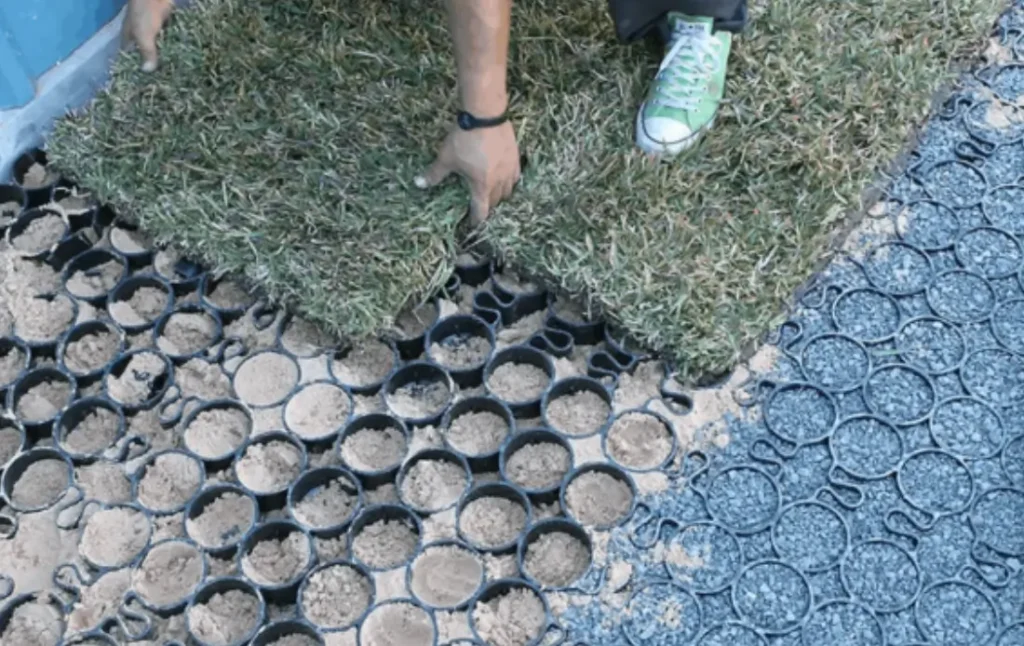

I will break the job into plain steps. I will also show layer thickness, materials, and checks that inspectors accept. You can hand this to your crew and get a clean outcome.
What is a grassland grid?
Green parking often fails because the soil pumps under wheels. You need a structure that spreads load and lets roots breathe.
A grassland grid is a cellular panel that spreads wheel loads over a wider area while keeping open cells for grass. It locks into a stable mat, supports traffic, and protects roots and crowns.
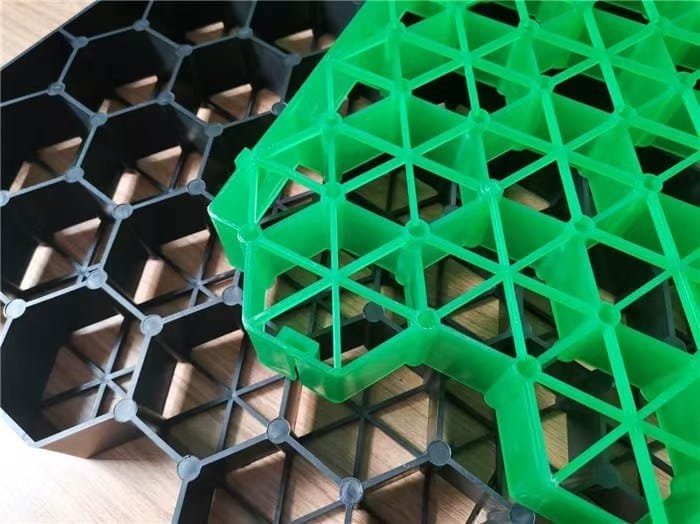
What the panel does
A grass grid works as many small beams. Each cell wall takes load and moves it sideways into the base. The open cell keeps space for air, water, and root growth. The panel also stops lateral soil movement, so the surface does not rut. In summer, the soil does not bake as hard as a closed paver. In winter, the cell walls protect crowns from shear.
Typical sizes and specs
You will see square or honeycomb cells. Common panel sizes are 500 × 500 mm or 600 × 400 mm. Cell heights range from 30–50 mm for cars and 60–80 mm for heavy service lanes. Designers will ask for compressive strength per unit area. Many panels rate above 200–400 t/m² when tested on a flat plate. More important in the field is the base thickness and compaction. The best panel cannot save a weak subgrade.
| Parameter | Typical value | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Cell height | 40–60 mm | Controls soil depth for roots and shear path |
| Panel size | 500 × 500 mm | Small panels speed curves and infill |
| Wall thickness | 2.0–3.5 mm | Higher wall resists wheel edge loading |
| Compressive rating | 200–400 t/m² | Lab figure; check base design as well |
| UV stability | ≥ 3% carbon black | Keeps panel from embrittlement outdoors |
Base interaction
The panel needs a stable, free-draining base. I use graded aggregates to carry load and move water away from roots. I place a non woven geotextile between subgrade and base when I need separation and filtration. I use a woven geotextile when I need extra tensile support over soft ground. This mix of geograde layers keeps fines from pumping and keeps the base clean for years.
How can grass grids be applied to parking lots?
Most green lots fail at entries, aisles, and turning spots. These zones see high shear and stop-start loads.
A grass grid turns a lawn into a traffic surface by adding structure and drainage. I design the base by traffic class, then divide the lot into zones and detail each layer and edge.
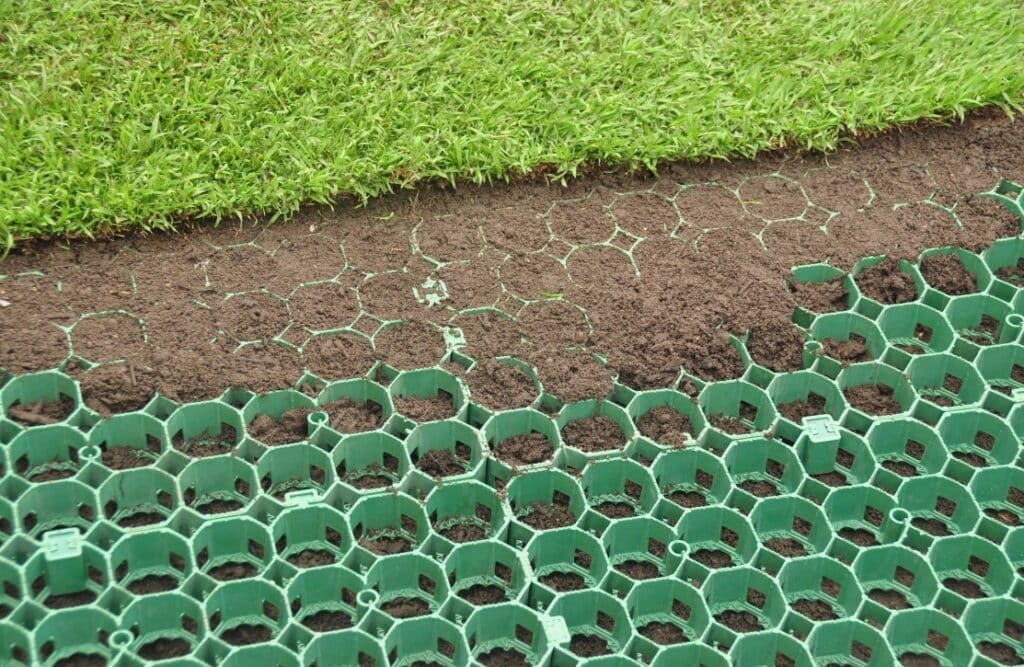

Use cases by zone
I split the lot into three zones: stalls, drive aisles, and fire/overflow. Stalls see low turning. Drive aisles see shear and braking. Fire lanes see point loads from outriggers or heavy axles. I increase cell height and base thickness in aisles and fire lanes. I also add stronger edge beams at entries to stop panel creep.
| Zone | Panel height | Base thickness (well-compacted) | Surface infill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stalls (cars) | 40–50 mm | 150–200 mm graded aggregate | 60–70% soil, 30–40% sand mix |
| Drive aisles (cars/light trucks) | 50–60 mm | 200–250 mm graded aggregate | Soil-sand with stabilizer if turning is heavy |
| Fire/maintenance lane | 60–80 mm | 250–350 mm graded aggregate | Soil-sand; consider turf reinforcement mesh on top |
Step-by-step build
- Survey and mark levels. Set falls at 1.5–2.0% toward drains or swales.
- Excavate to design depth. Remove topsoil and weak pockets. Proof-roll and mark soft spots.
- Stabilize soft spots. Use a woven geotextile plus extra aggregate to bridge.
- Place separation layer. Use non woven geotextile over the subgrade for filtration.
- Build the base. Place graded aggregate in 100 mm lifts. Compact to ≥ 95% of modified Proctor or as your spec lists.
- Screed bedding. Place 20–30 mm of sharp sand or a soil-sand blend to receive panels.
- Lay panels. Start along a straight edge. Stagger joints. Use in-built clips to lock. Trim with a saw where needed.
- Anchor edges. Use concrete edge beams or steel/aluminum edging. Entries need the strongest restraint.
- Fill cells. Use a blend of topsoil and washed sand. I often use 60:40 to keep pores open. Compact lightly.
- Water and settle. Top up infill after first water.
- Seed or turf. For fast turnover, lay turf rolls cut to cell size. For seed, choose a mix with traffic-tolerant rye and fescue.
- Establish. Keep traffic off until turf roots bind. For seed, allow 4–6 weeks in warm seasons.
Drainage and soil
Water and air must move. I avoid heavy clay in infill. I add sand to get open pores and faster recovery after rain. I check that subdrains or soakaways can handle peak events. If the lot is flat, I do not block movement under the surface. I add a perforated pipe where needed.
What buyers call this product
In tenders and RFQs, many names appear. I list them here so your search team catches all leads: grass grid, grid grass, grass grid system, grass driveway grid, grass grid driveway, driveway grass grid, grid grass driveway, driveway grid grass, grass drive grid, grass protection grid, grass support grid, grass square grid, grid for grass, the grass grid, grass create grid, grass driveway grid installation, grass driveway grid system. All point to the same class of product with small spec changes.
What are the common materials used for grass grid systems?
Material choice changes heat resistance, impact strength, and price. Buyers want a clean comparison with clear trade-offs.
Most grass grids use recycled HDPE or PP copolymer. Concrete units exist for very high loads, but they reduce green cover and increase heat.
Plastic options
HDPE panels use high-density polyethylene. They flex without cracking and take impact well. HDPE keeps toughness in cold weather. It also accepts recycled content, which cuts cost and helps certifications. However, HDPE softens at lower temperatures than PP. On hot days, a thin-wall HDPE panel can creep under high point loads unless the base is strong.
PP panels use polypropylene, often a copolymer for impact. PP has a higher heat deflection temperature than HDPE. It holds shape better under summer loads. It can be stiffer, which helps at entries. In very cold regions, pure PP can get brittle if the blend is not tuned. Good suppliers add impact modifiers and UV packages.
Concrete grass pavers are very strong in compression. They carry heavy trucks with thin bases on firm subgrades. They reduce green cover in practice, because cells are small and edges are wide. They store heat. They break if the subgrade settles or frost heaves. They also need more cutting and labor around curves.
| Material | Strength profile | Heat/cold behavior | UV/aging | Sustainability | Typical use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled HDPE | High impact, good flex | Softer in heat, tough in cold | Good with carbon black | Excellent recycled content | Car parks, paths |
| PP copolymer | High stiffness, good impact | Better hot stability | Good with UV package | Recyclable; less recycled content used | Aisles, entries |
| Concrete | Very high compression | Heat island risk; brittle on heave | No UV issue | High mass; long life | Fire lanes, industrial |
Additives and color
I prefer black or dark green for UV stability. Carbon black at 2–3% absorbs UV and protects polymer chains. Green masterbatch needs its own UV package or a co-extruded cap. Check the pigment supplier’s outdoor data. Ask for an accelerated weathering report.
Quality checks
Request a compressive test method and report. Ask for panel wall thickness tolerance, cell height tolerance, and impact drop test. Check tab strength for the locking clips. Ask for a pull-out value for turf reinforcement if the panel includes barbs. A short mill certificate with batch traceability helps audits later.
FAQ
Q: Can a grass driveway grid handle SUVs and light trucks?
A: Yes. Choose 50–60 mm cells and a 200–250 mm base on firm subgrade. Use strong edges at entries and turning spots.
Q: Will snow plows damage the panels?
A: Use shoes on blades and set height above crowns. Panels sit below the grass tips when filled. Many sites run plows with no harm.
Q: How do I maintain the surface?
A: Aerate light, top-dress with sand-soil, seed thin areas, and block traffic during saturation. Sweep sediment off entries after storms.
Q: Can fire trucks use grass protection grid lanes?
A: Yes with design. Use 60–80 mm cells, 250–350 mm base, and strong edges. Confirm axle loads and outrigger pads in design.
Q: Do I need geotextile under the base?
A: In most soils, yes. A non woven geotextile stops fines from pumping and keeps drains open. Use a woven geotextile where subgrade is very soft.
Q: What seed mix works best?
A: Use traffic-tolerant rye and fescue blends. Add a small percent of micro-clover if the client accepts mixed sward and lower fertilizer.
Q: How fast can I open to traffic?
A: Turf opens fastest. Seed needs 4–6 weeks in warm seasons. If you must open early, protect with barriers or run only straight-line moves.
Q: Does irrigation help?
A: Yes. Light, frequent cycles in the first month help roots fill cells. After that, shift to deeper, less frequent watering.
Conclusion
A strong base, a stable panel, and open, living infill make a green lot that lasts. Build by zone, protect edges, and keep water moving.





