Geotextiles are permeable synthetic fabrics engineered for soil separation, filtration, drainage, and erosion control in civil and environmental projects.
Our geotextiles provide high tensile strength, durability, and consistent performance, making them suitable for applications in infrastructure, landscaping, agriculture, and coastal protection.
Discover Our Best Geotextiles Collection

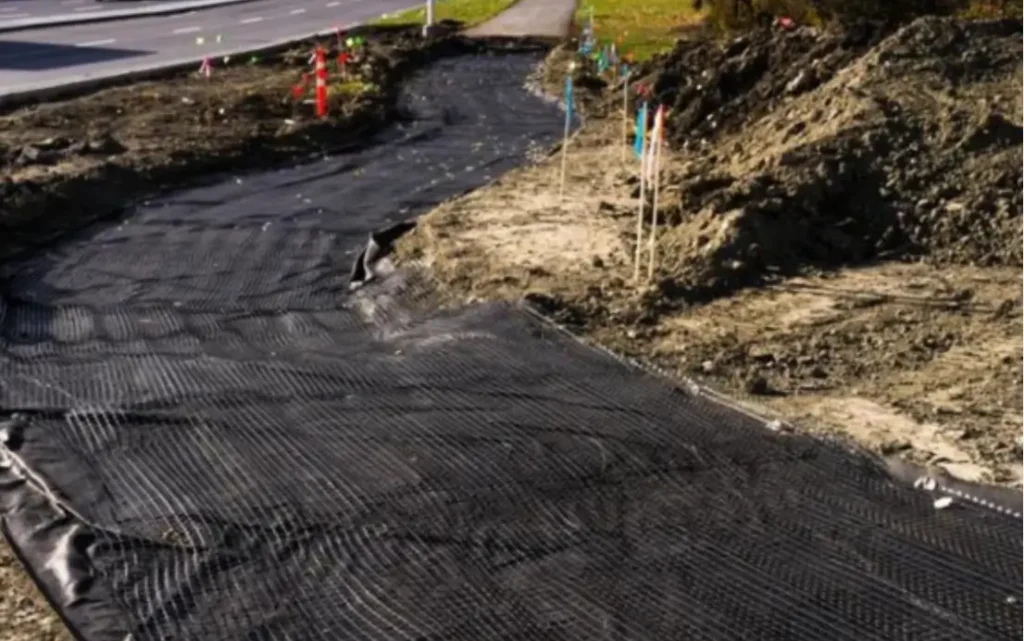
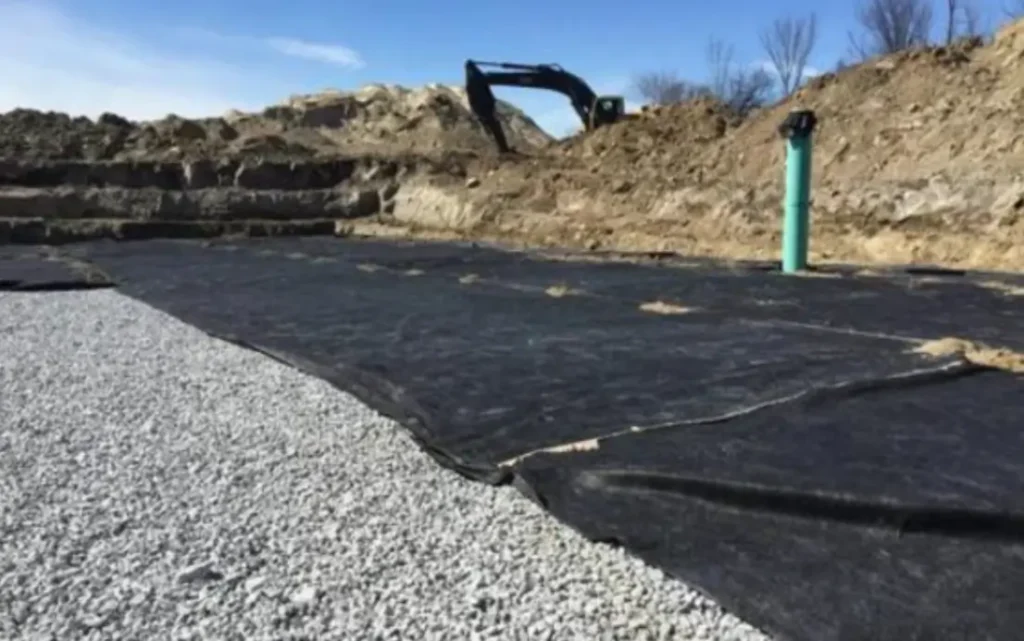
Engineered from high-quality staple fibers and densely needle-punched for uniform permeability, this nonwoven excels in filtration, separation, drainage, and cushioning. You get robust puncture resistance, stable water flow under load, and strong survivability under aggregates-ideal beneath roads, rail ballast, geomembranes, and revetments.
Constructed from high-tenacity polypropylene tapes, this woven delivers high tensile strength with low elongation for cost-effective subgrade stabilization and reinforcement. It controls fines migration, improves bearing capacity, and withstands harsh site conditions with excellent chemical and UV resistance-a proven choice for haul roads
yards, ports, and platforms.

Types of Geotextiles
Supported by our professional manufacturing capability and rigorous quality standards, We supply a wide selection of geotextile products to address diverse project needs. Explore our range to find the ideal solution for your application.
By Materials

Polypropylene geotextile is made from high-quality polypropylene material, offering excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and durability. It is widely used in separation, filtration, drainage, and erosion control applications, especially in environments requiring resistance to acids, alkalis, and microorganisms.
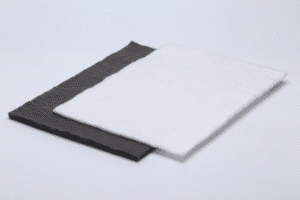
Polyester geotextile is produced from high-tenacity polyester fibers, providing high tensile strength, superior UV resistance, and exceptional resistance to deformation under load. It is commonly applied in road reinforcement, subgrade stabilization, embankment support, and other engineering projects requiring long-term performance under demanding conditions.
By Process
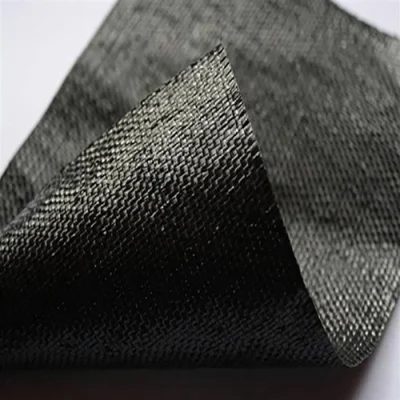

Woven geotextile is manufactured by interlacing polypropylene or polyester yarns in a regular pattern, resulting in a high-strength fabric with low elongation. It offers excellent tensile strength, puncture resistance, and soil separation capabilities, making it ideal for reinforcement applications in roads, embankments, and foundations.
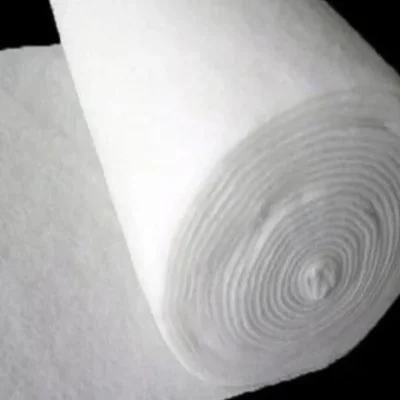

Non woven geotextile is produced by mechanically or thermally bonding synthetic fibers, creating a permeable felt-like fabric. It provides superior filtration, drainage, and erosion control properties, and is commonly used in subsurface drainage systems, landfill leachate collection, and as a protective layer in various civil engineering projects.
By Materials
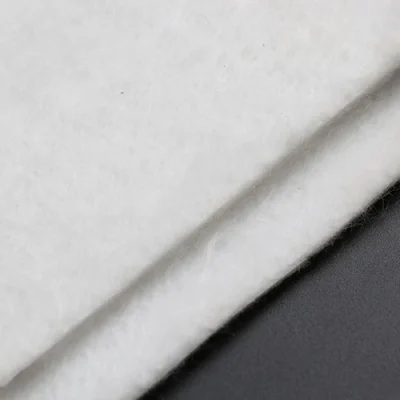

Filament Geotextiles
Filament geotextiles are made from continuous synthetic filaments that are layered and bonded into a stable network. This structure provides high tensile strength, puncture resistance, and consistent permeability, offering excellent performance in reinforcement, separation, and filtration for applications such as road bases, railways, and coastal protection.
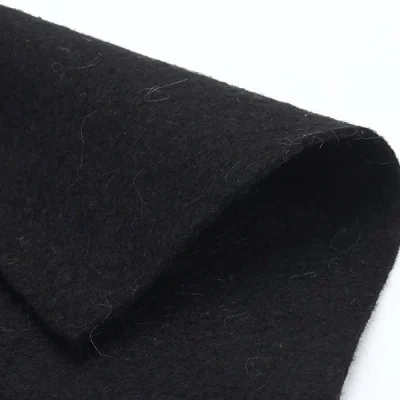

Short-filament geotextile is produced from staple fibers that are carded and bonded to form a uniform non-woven fabric. It offers good permeability, filtration, and drainage properties, along with soft texture and adaptability to subsoil movements. It is widely used in drainage systems, landscaping, erosion control, and as a protective layer.
Advantages of Geotextiles
The following geotextiles advantages make them a superior choice to alternative geosynthetic materials:

Improved Drainage
Geotextiles promote drainage by letting water to move through, which stops water from accumulating.

Ease of Installation
The installation of geotextiles is made easier as they do not require additional layers of soil aggregates to provide extra reinforcement.

Versatility
Geotextiles can be used in a wide range of applications and are can be manufactured to meet your specific project needs.

Better Filtration and Separation
Geotextiles act as filters as they allow water to pass through while preventing soil particles from migrating.

Cost-Effective
Geotextiles are more affordable compared to other materials as their use reduce the need for extensive excavation and traditional construction materials.

Enhance Soil Stability
By limiting soil particle mobility and so improving soil stability, geotextiles act as reinforcement for the soil. Thereby reducing soil erosion and improves load bearing capacity.
Our nonwoven geotextiles fabrics are manufactured using advanced bonding technology with high-quality polyester and polypropylene. Known for high permeability and durability, they are trusted worldwide in drainage, soil stabilization, and filtration projects.


Woven geotextiles are manufactured by weaving fibers in parallel or perpendicular orientations, creating fabrics with high tensile strength, low elongation, and excellent permeability. Ideal for soil stabilization, reinforcement, and road construction.
As a trusted supplier of heat bonded geotextiles, we deliver ISO-certified nonwoven fabrics engineered for filtration, underlayment, and erosion control. Designed with chemical resistance and durability for civil engineering and construction applications.


As a trusted composite geotextile supplier, MJY manufactures ISO-certified fabrics engineered for road construction, slope stabilization, and retaining wall reinforcement. Strong, durable, and cost-effective geotextile solutions.


Geotextiles are commonly manufactured using polypropylene and polyester, although both synthetic and natural fibers can be selected depending on project requirements. These materials ensure geotextile fabrics provide durability, separation, filtration, and reinforcement in different construction applications.
Natural Fiber Geotextiles
Biodegradable natural fabrics are often used as short-term erosion control solutions until vegetation takes root. The most common natural fibers include:
Jute: A flexible, fast-decomposing fiber that enriches soil with nutrients after biodegradation. While standard jute geotextiles have a short lifespan, treatments and blending methods can extend their durability up to 20 years, offering customized permeability and strength for landscaping and erosion control projects.
Coir: Manufactured from coconut husk fiber, coir is one of the strongest natural fibers available. Coir geotextiles protect slopes, stabilize soil, and promote rapid vegetation growth, making them an effective eco-friendly option for erosion control and landscaping.
Synthetic Fiber Geotextiles
Synthetic polymers remain the primary raw materials for modern geotextile manufacturing, particularly for woven and nonwoven fabrics. These offer consistent strength, high filtration performance, and long service life. Commonly used polymers include:
Polyamide (Nylon 6,6 and Nylon 6): Though strong, polyamides are less preferred due to higher cost and weaker performance compared to other fibers.
Polyester (PET): Known for high tensile strength, creep resistance, and durability at elevated temperatures. However, PET geotextiles are less suitable in highly alkaline soils (pH > 10) due to hydrolytic degradation.
Polyethylene (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE): HDPE fibers are especially valuable for geotextile weed barriers and drainage applications due to their crystalline structure and chemical resistance.
Polypropylene (PP): The most widely used polymer in geotextile membranes, PP offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and cost-effectiveness. However, it is sensitive to UV radiation and high temperatures, requiring protective measures in outdoor projects.
Geotextile Vs Geomembrane
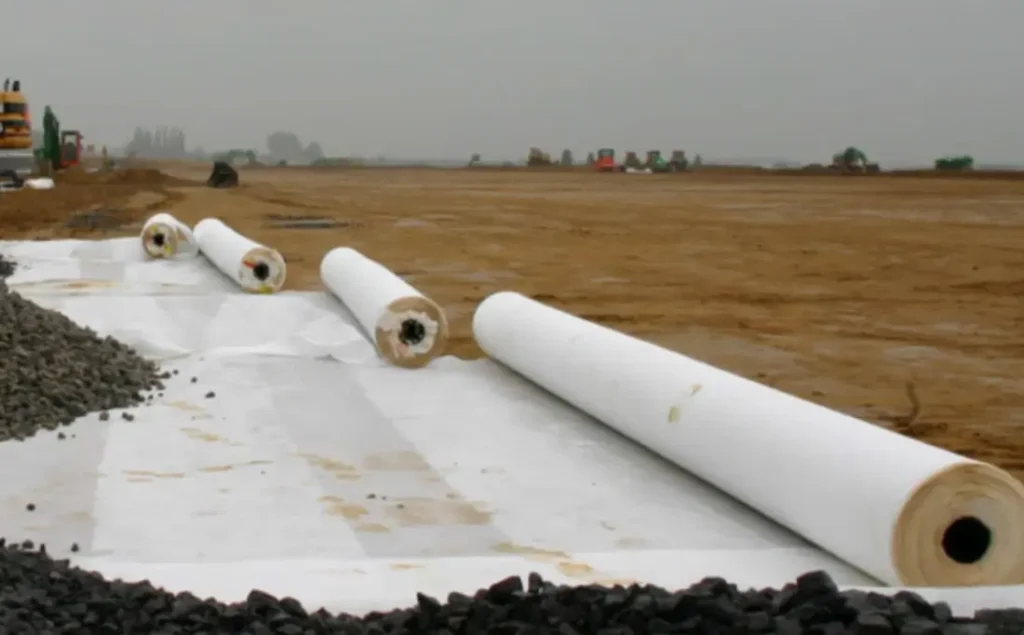
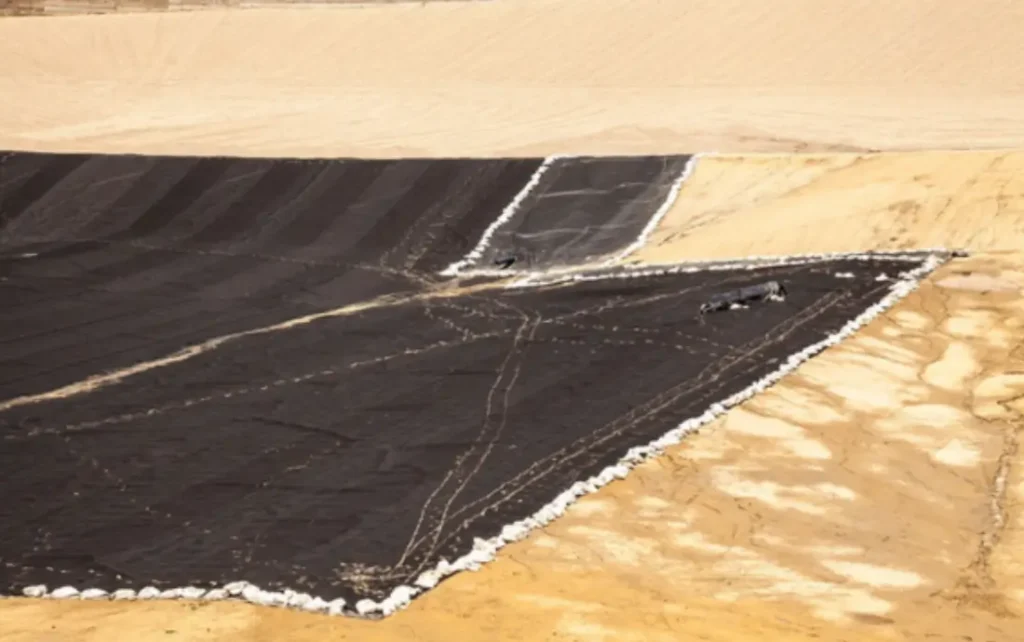


Geomembrane vs Geotextile: Key Differences in Geosynthetics
Geomembrane and geotextile are both geosynthetic materials widely used in civil engineering, but they serve very different functions despite both being polymer-based.
Material & Permeability
Geotextiles are porous fabrics made from synthetic fibers through knitting or needle punching. Their permeability allows water to pass while blocking soil, making them ideal for drainage, filtration, and erosion control.
Geomembranes, in contrast, are impermeable sheets manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other polymers. They act as waterproof barriers in projects where seepage prevention is critical.
Functional Features
Geotextile Fabrics offer excellent performance in separation, drainage, filtration, reinforcement, and anti-seepage applications. They are lightweight, heat-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and maintain strength under freezing conditions.
Geomembrane Liners provide non-porous, long-lasting protection. Their functions include foundation stabilization, crack resistance, and reliable seepage control.
Applications
Both geotextiles and geomembranes are essential in civil engineering groundwork but are used differently:
Geotextiles are applied in soil separation, subsurface drainage systems, erosion control, filtration layers, and as underlayment for roads and landscaping projects.
Geomembranes are primarily used where waterproofing and contamination prevention are crucial. Common uses include landfill liners and caps, groundwater protection, canal and pond liners, hydroponic systems, foundation wall liners, and other environmental containment projects.
Differences Between Geotextile Vs Geogrids


Geotextiles and geogrids are both types of geosynthetic materials widely used in geotechnical and civil engineering projects. While they may overlap in certain applications such as soil stabilization or reinforcement, they differ significantly in structure, function, and performance. The comparison below highlights the main differences between geotextile fabrics and geogrids:
| Parameter | Geotextile | Geogrid |
|---|---|---|
| Composition and Structure | Mostly produced using woven or nonwoven synthetic fiber of polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester. It is often a flexible and pervious fabric-like material, which permits passage of water. | Constitute polymer materials like polyethylene or polyester, though has a grid-like structure having holes. It has semi-rigid or rigid structure and is generally tougher than geotextile fabric. |
| Function | Primarily act as drainage, filtration and/or separation layers within civil and geotechnical engineering projects. Geotextile membranes can prevent materials from mixing, allow drainage of fluids, control soil erosion, and segregate different layers of soil. | Majorly serves as a reinforcement material. Geogrids give tensile strength and boost soil structure stability through load distribution and soil movement minimization. |
| Load Distribution and Strength | The load distribution mechanism is mainly via stress transfer and friction. Geotextile fabric materials are not perfect for load-bearing roles and exhibit limited tensile strength. | Specifically designed for high load distribution and tensile strength. Geogrid materials are capable of transmitting forces across a broader area and bear considerable loads. This makes them appropriate for reinforcement applications. |
| Application Areas | The geosynthetic fabrics are ideal for geotextile fabric for driveways, filtration and drainage systems, garden geotextile and erosion control applications. | Commonly applied in applications involving soil reinforcement like pavement construction, retaining walls, embankments, and steep slopes. |
Physical Properties of Geotextile


Specific Gravity
Specific gravity measures the density of a geotextile compared to water. A geotextile with a specific gravity greater than 1 is denser than water and sinks, while one with a specific gravity below 1 will float. This property is crucial for applications where buoyancy plays an important role.
Thickness
Thickness refers to the distance between the two surfaces of a geotextile, typically measured in millimeters (mm) or inches (in). Thicker geotextile fabrics usually deliver higher strength, durability, and longer service life in construction and engineering projects.
Stiffness
Stiffness describes the ability of a geotextile to return to its original shape after being exposed to external forces. Projects built on irregular or uneven surfaces often require geotextiles with strong stiffness for proper performance and stability.
Density
Density is the mass of a geotextile per unit volume, usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). High-density geotextiles provide excellent resistance to penetration and smaller pore spaces, while low-density geotextiles offer greater porosity and improved water flow capacity.
Mechanical Properties of Geotextile


Tenacity
Tenacity refers to the tensile strength of a geotextile per unit cross-sectional area. It measures how well the material resists stretching or pulling without deformation. A geotextile with high tenacity provides superior reinforcement, stability, and long-term performance in demanding civil engineering projects.
Flexibility
Flexibility is the ability of a geotextile membrane to bend or conform to different shapes without breaking. Flexible geotextiles are highly adaptable, making them ideal for irregular construction sites, uneven soil surfaces, and applications that require easy installation.
Compatibility
Compatibility defines how effectively a geotextile performs when combined with other geosynthetic or construction materials. A compatible geotextile integrates seamlessly with geomembranes, concrete, or sand aggregates, ensuring structural integrity and reliable functionality in composite applications.
Tear Resistance
Tear resistance is the geotextile’s ability to withstand tearing, puncturing, or mechanical damage. Fabrics with high tear resistance are more durable during installation and perform better under heavy loads, sharp aggregates, or high-stress conditions.
Frictional Resistance
Frictional resistance is the property that prevents geotextile fabrics from slipping or sliding when subjected to external forces. This feature enhances interlocking performance, improves soil stabilization, and ensures the geotextile remains securely in place when used with other construction materials.
Hydraulic Properties of Geotextiles


Porosity
Porosity refers to the number of openings or voids within a geotextile fabric. It determines the material’s capacity to transmit water, air, and other fluids. Geotextiles with higher porosity feature more interconnected pores, which allow greater water flow and enhanced drainage. This makes them ideal for erosion control, filtration layers, and subsurface drainage applications where efficient water movement is required.
Permittivity
Permittivity is the hydraulic property that measures how effectively a geotextile fabric allows water to flow through its plane under pressure. A geotextile with high permittivity facilitates rapid cross-plane water movement, preventing hydrostatic pressure buildup behind retaining walls, slopes, or drainage systems. This ensures long-term stability, effective drainage, and reduced water-related structural risks.
Selection of Geotextile for Civil Engineering Projects

Function
Specify the primary function of the geotextile as it may serve a number of purposes. Recognizing the planned use of geotextile membrane will be instrumental in selecting the right type.

Cost
Analyze the geotextile material cost-effectiveness by considering the entire project cost. Moreover, it is important harmonizing the expenses with the desired efficiency and durability of the material.

Strength Ratings
There are numerous categories of geotextile fabrics depending on their strength. Normally, every project specification dictates the suitable category, which is relies on the amount and size of fill you will use.

Strength Ratings
There are numerous categories of geotextile fabrics depending on their strength. Normally, every project specification dictates the suitable category, which is relies on the amount and size of fill you will use.

Soil Type
You will require a tougher, thicker type of geotextile, which guarantees that it does not get punctured by the fill. For applications on firmer soils, like geotextile arena footing, a thinner fabric is will be adequate for the function.

Permeability
Asses the preferred geotextile permeability, which ought to be in harmony with the rate of fluid flow within the project. Select a fabric with the right permeability to facilitate efficient filtration or drainage.

Fill Size
To avoid puncturing, you will need thicker material for bigger and heavier fill. For geotextile fabric under pavers, the fill size typically ranges between 20mm-150mm, though they can have diameter of up to 400mm.

Compatibility
Ensure that the geotextile membrane is in harmony with additional materials employed, like aggregates, other geosynthetics, or soils. Compatibility of the material is vital as it guarantees correct functioning and long-run efficiency of the geotextile system.

Longevity
Consider the anticipated project lifespan and choose a geotextile fabric material that guarantees desired degradation resistance and durability. You should factor in parameters like resistance to microbial deterioration, aging resistance, and UV resistance.
How to Choose the Right Geotextile Size
Both woven and nonwoven geotextile fabrics are usually supplied in large rolls of varying widths and lengths. The exact geotextile size depends on project requirements, installation methods, and the manufacturer’s production standards.
- Width: Standard widths generally range from 1m to 6m, though wider rolls are available for large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Length: Roll lengths typically vary between 15m and 150m or more, depending on fabric type and supplier.
- Custom Options: Many manufacturers provide customized geotextile dimensions tailored to specific site conditions or engineering needs.
When selecting, always match the geotextile roll size with your project’s ground conditions, ease of installation, and overall design specifications. Consulting with geotextile suppliers or manufacturers ensures you get the most effective size for your application.
Understanding Geotextile Lapping Length
The lapping length is the overlap distance between adjacent geotextile sheets or rolls during installation. Proper lapping is essential to guarantee seam integrity, barrier function, and structural strength.
- Leakage Prevention: Adequate lapping creates a continuous barrier, reducing the risk of soil migration or water leakage.
- Load Distribution: Correct overlap helps distribute loads evenly, improving the geotextile’s strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Uniformity: A proper lapping length ensures a consistent geotextile layer, enhancing performance across the entire surface.
Factors Affecting Lapping Length:
- Geotextile Properties (mechanical, physical, hydraulic performance)
- Design Requirements (application type, reinforcement needs)
- Site Conditions (soil type, slope gradient, load expectations)
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations to maximize geotextile performance and durability.
Main Applications of Geotextile Fabrics
Separation
Geotextiles prevent the mixing of two different soil layers. For example, in road construction, a geotextile underlayment separates coarse aggregate from fine subgrade, maintaining long-term road stability.
Stabilization
By spreading geotextile membranes over soft or compressible soils, the material allows water drainage while consolidating the soil, improving stability for embankments, roadbeds, or construction platforms.
Reinforcement
Geotextiles enhance structural strength in demanding applications such as:
- Steep slopes – enabling sharper inclines without soil erosion.
- Retaining walls – improving settlement handling and structural integrity.
- Erosion control – protecting sea embankments, shorelines, and reclaimed land projects.
Filtration
Geotextiles allow water to pass through while retaining soil particles. This is vital in applications such as drainage trenches, retaining walls, and flood defense systems, where soil stability must be preserved.
Drainage Systems
Nonwoven geotextiles are widely used to collect and channel liquids to designated discharge points. They are key components in subsurface drainage and landfill leachate systems.
Sealing
When impregnated with asphalt or bitumen, geotextiles act as impermeable membranes, preventing contamination of groundwater and reducing potable water loss. This makes them effective for environmental protection projects.
How Long Does Geotextile Last?
The environmental conditions, geotextile quality, and distinct use can influence the geotextile fabric lifespan. Their design generally enables them to guarantee long-term performance and durability in civil and geotechnical engineering applications.
Typically, geotextiles fabric materials can serve for as long as 200 years, dependent on their planned use and the conditions you install them. The polymers used in their manufacture have a great molecular structure, mechanical properties and are able to resist degradation.
What are the Disadvantages of Geotextile?
Geotextiles have certain limitations that reduce their potential to provide optimal performance for your projects. The disadvantages are;
- Vulnerability to degradation by UV radiation
- Limited Strength for Heavy Loads
- Potential Clogging in Filtration Applications
What is the Opening Size of Geotextile?
There is a broad range of Geotextile opening sizes to handle the various drainage, separation and filtration needs. On this account, choose a geotextile fabric with the right aperture opening size that ensures its efficiency in the purposed application.
Popular geotextile opening sizes span from as tiny as 0.07mm to several millimeters. Nonetheless, specific projects might need geotextile fabrics with varying opening sizes dependent on the preferred separation or filtration requirements.
How much is Geotextile Price?
Geotextile fabric price can vary based on a number of variables including weight, thickness and type of geotextile, quantity being bought, and brand. Moreover, the availability and prevail market conditions can also affect the price of geotextile material.
Typically, geotextiles fabrics are sold per square foot/meter or by the roll. The geotextile price range can differ broadly from $0.5 – $5 for every square meter. These are estimated price and might not represent the prevailing market prices.
MJY is a trusted geosynthetic manufacturer for over 10 years with our expertise and vast knowledge in the industry.
