Geocell
Mu Jin Yuan Geocell are strictly engineered to meet the building and construction codes. We carefully choose material and invest in modern technology for optimal performance.
- Best soil stabilization properties
- High grade material for optimal performance
- Available in perforated and non-perforated options
- Specification Generator Tool
- Case Studies/Pictures/Videos
Geocell
Geocell is a 3D synthetically produced material constructed from polymeric strips assembled in a honeycomb design. It serves as a confinement system instrumental in securing construction materials, including sand, aggregate infill and soils to offer load support and prohibit erosion. Although initially developed for military roadways, geocells applications are now widespread in vehicular and foot traffic construction projects.
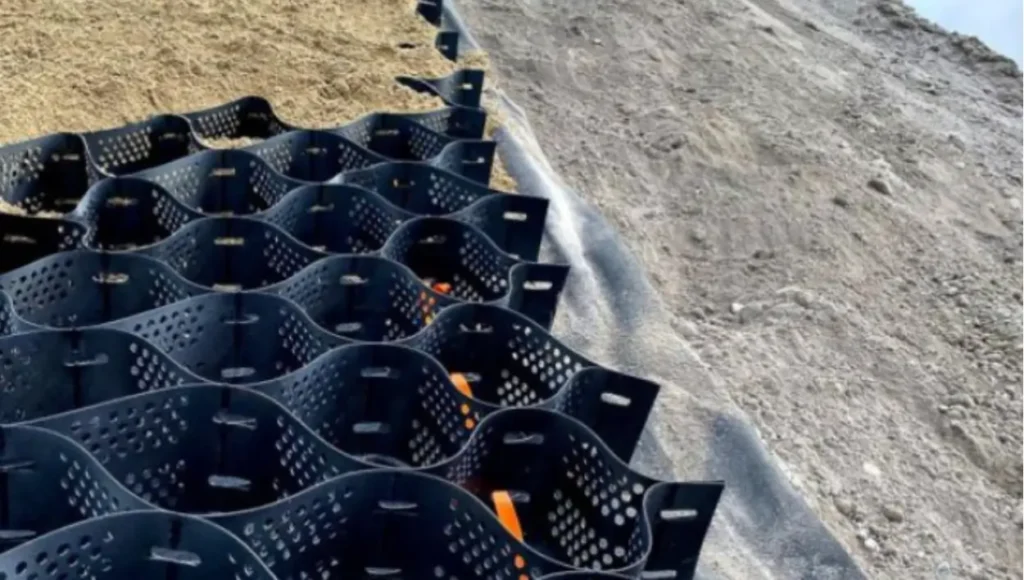
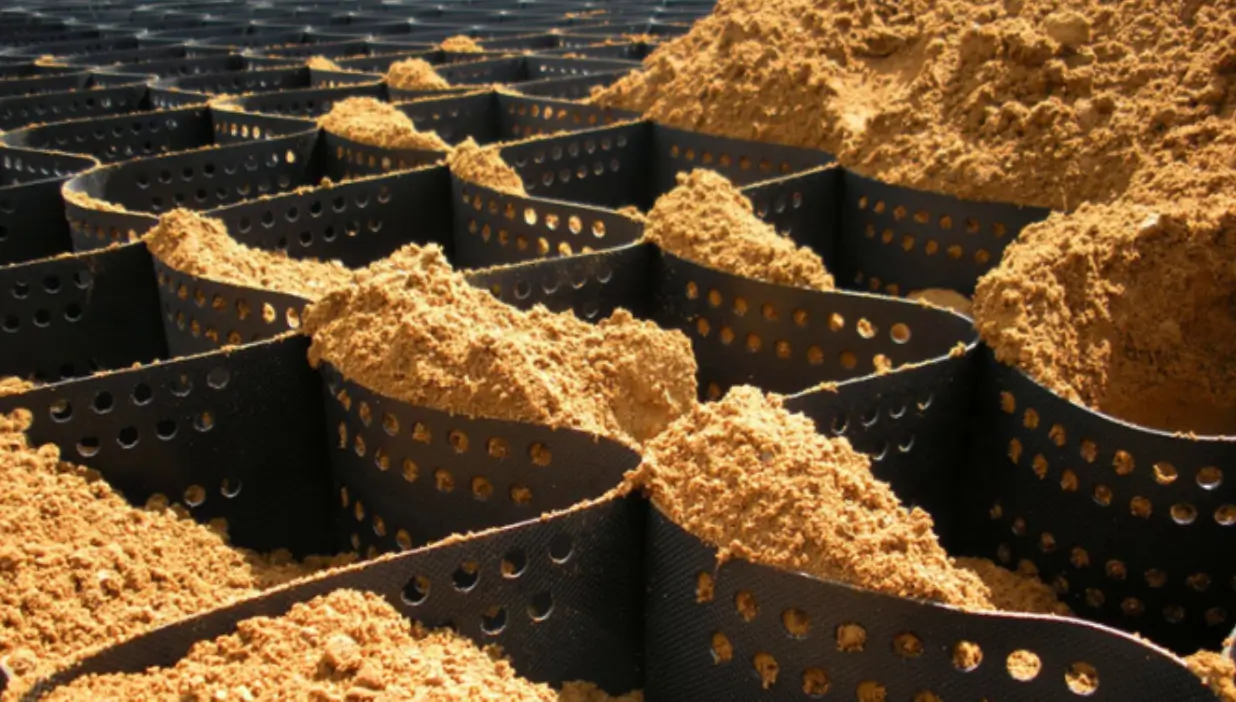
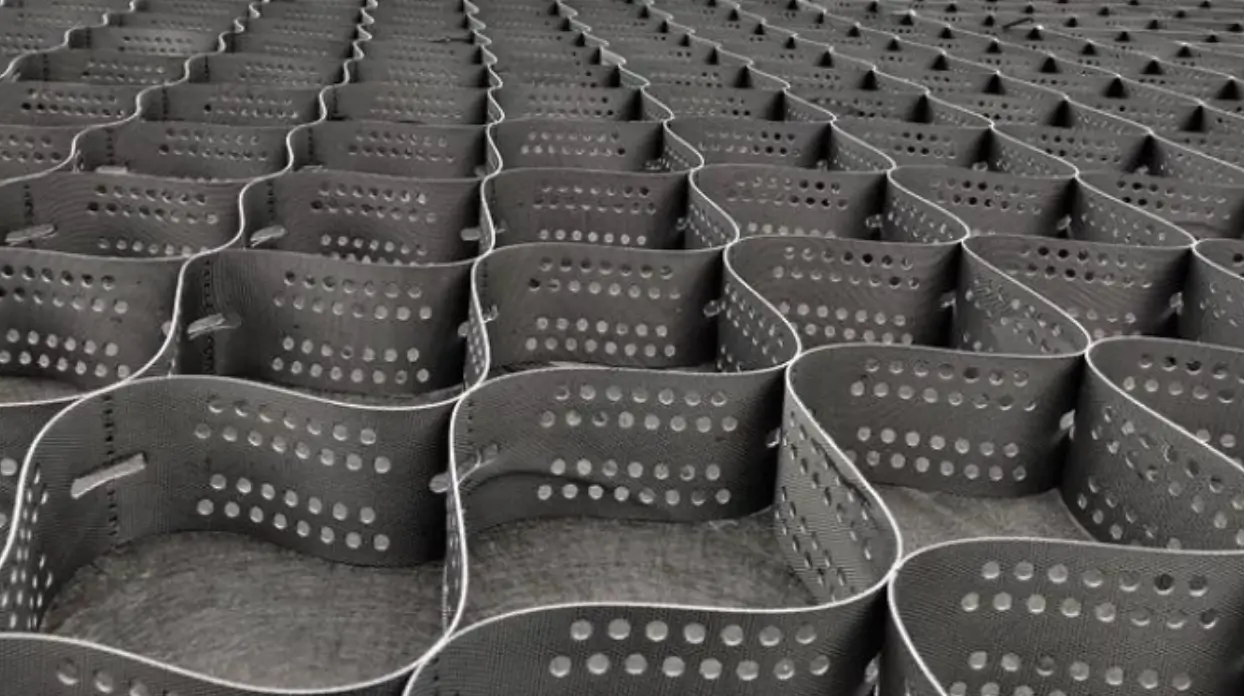
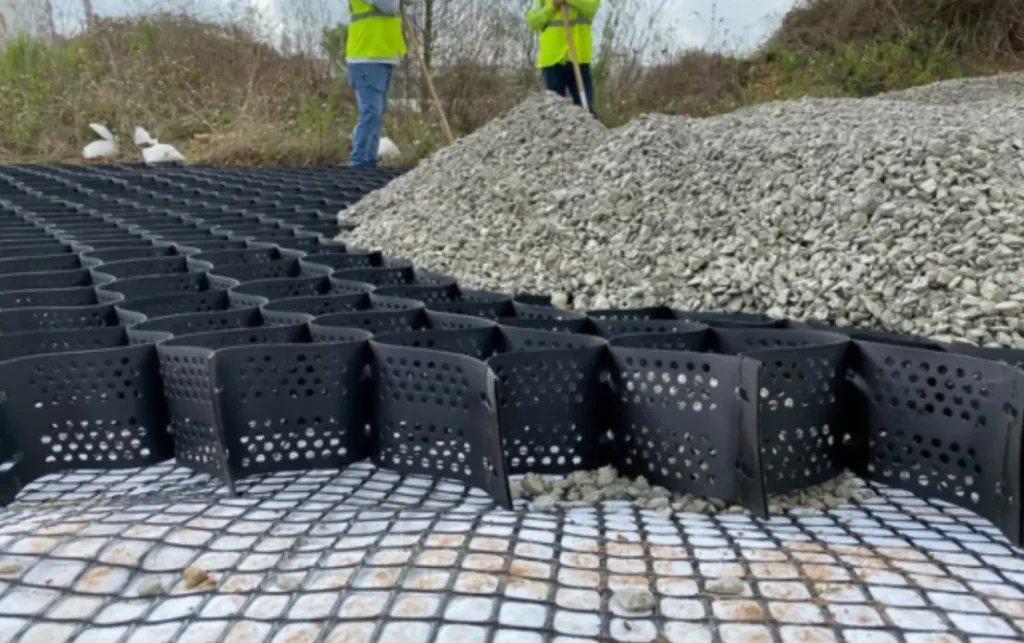
Perforated Geocells
The wall of each cell within a perforated geocell system features a series of uniformly spaced, minute openings that help disperse stress and minimize disfigurement. The material’s structural integrity relies heavily on the rigidity of the weld and the strip.
The punctured and textured surface raises the angle of friction between the cell wall and aggregate infill. This promotes better aggregate confinement and higher general load distribution. Moreover, the perforations allow for lateral chamber-to-chamber drainage of excess surface and ground water, minimizing the adverse impacts of trafficking above saturated soils.


Non-Perforated Geocells
Also referred to as solid wall geocells, non-perforated geocell confinement systems lack any openings across the cells wall. They are suitable for applications in which drainage of water is not a major consideration.
You can also employ them where there is need for infill materials containment inside the cells. The functions of non-perforated geocells are for reinforcement, load support, and stabilization of soil.
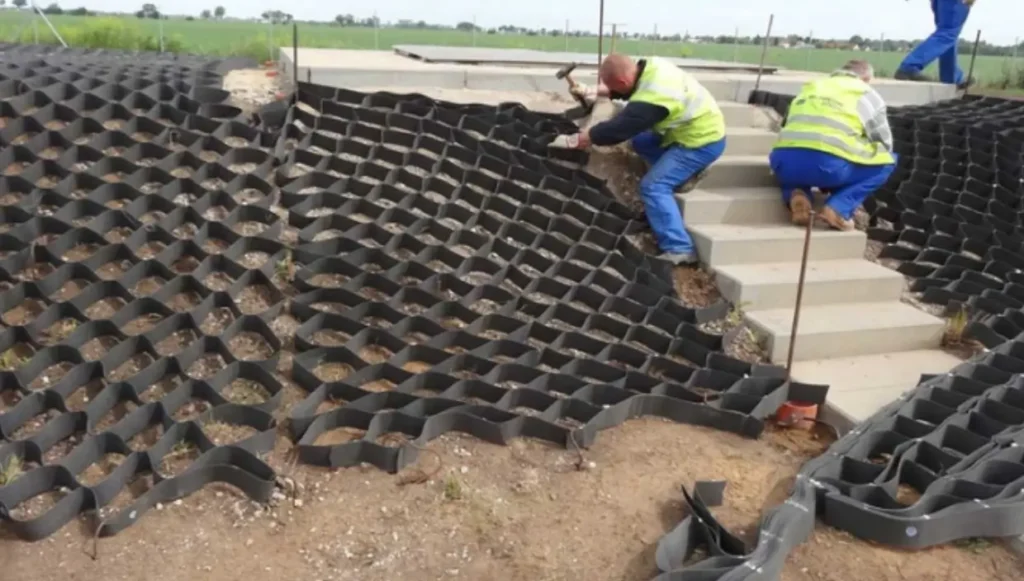
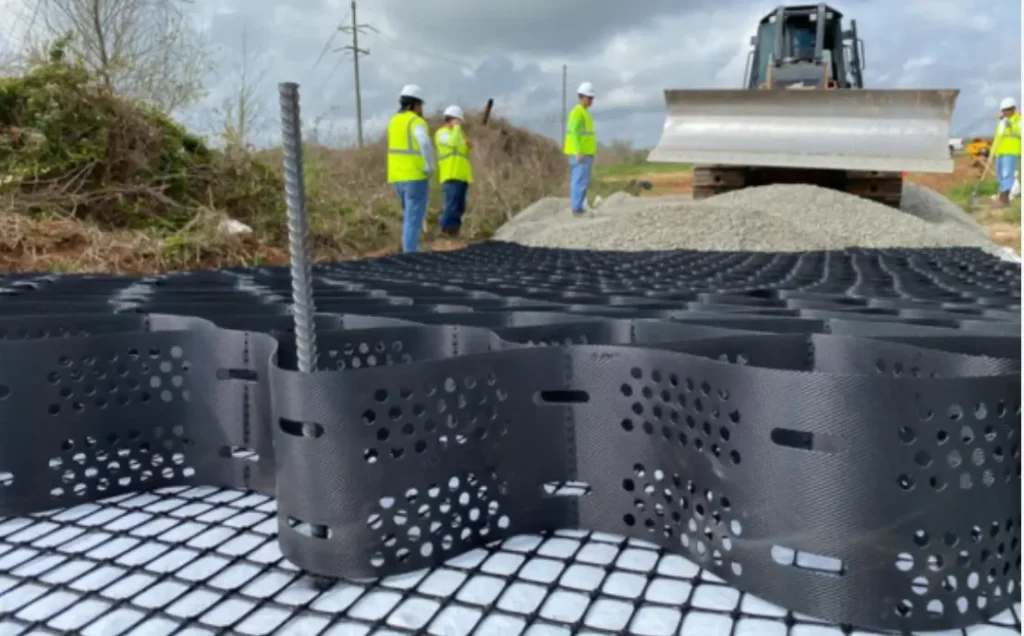
How to Install Geocells
Often, geocell grids come in collapsed state that is easy to expand. You can expand them fast and effortlessly, and place the infill manually, using simple construction equipment or tools.
Rectangular stretcher frames usually simplify the geocell installation process by expanding the dimensioned parts accordingly. The multipurpose stretcher frames help in ensuring correct sectional geometry, and are employed only during infilling.
Individual geocell parts can be coupled together through, stapling, anchoring, or using clip arms. For increasingly sophisticated constructions, extra fittings like tendons and anchoring devices might be necessary.

Geocell Technical Specification
There are several crucial geocell features that you should communicate to the geocell manufacturer or supplier when placing your order. Here are the geocell technical specifications that you must consider:
- Material
- Thickness
- Cell Depth
- Texture (textured, smooth, textured perforated)
- Panel Size
- Perforation (Yes/No)
- Colour
- Standard (ASTM, GSI, ISO)
Lifespan of Geocells
Geocells are manufactured to offer durable performance in various applications. The lifespan of geocells can vary depending on factors such as the quality of the material, installation techniques, environmental conditions, and the specific project requirements.
Polymers used in geocell manufacture like polyethylene and polypropylene are chemically inert and resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation and chemical degradation. Normally, on average, geocells can have a lifespan ranging from 20 to 50 years or more.

Smooth Geomembranes Vs Textured Geomembranes


Geocells manufacturers normally use a number of materials for production of the confinement systems. The material type utilized in geocells manufacturing considerably affect the performance, cost and durability of the product. Every geocell material possesses its individual pros and cons, and the selection relies on parameters like site conditions, project specifications, environmental aspects, and budget.
The common materials used in geocell production comprise of:
High-Density Polyethylene – HDPE is popular for its high chemical resistance, strength, and longevity. HDPE geocells are the most preferred because of their outstanding properties, consisting of resistance to moisture, chemical and ultraviolet radiation degeneration.
They are easy to mold into required honeycomb structure due to their flexibility. HDPE geocells grids offer superior confinement, stabilization, and load distribution abilities.
Polypropylene (PP) – Polypropylene is another thermoplastic polymer material for geocell manufacturing with properties same as those of HDPE. They commonly find application in projects where cost considerations or chemical compatibility are of great concern.
Polyester (PET) – Though polyester is not a common geocell material, it is still employed in some applications. Polyester geocell manufacturing often uses high-tenacity polyester fiber that is coated further using other polymer material.
Polyester geocells systems provide superior tensile strength and outstanding chemical and biological deterioration resistance. They are perfect for geocell applications needing greater rigidity and strength in comparison to HDPE geocells.
Recycled Materials – Some geocell manufacturers use recycled plastics in the production process to minimize environmental effects and encourage sustainability. They can utilize recycled PP or HDPE to produce geocells whilst retaining their fundamental properties. This helps in waste minimization and promote the circular economy concept.
Welding Techniques Used in Geomembrane Installation
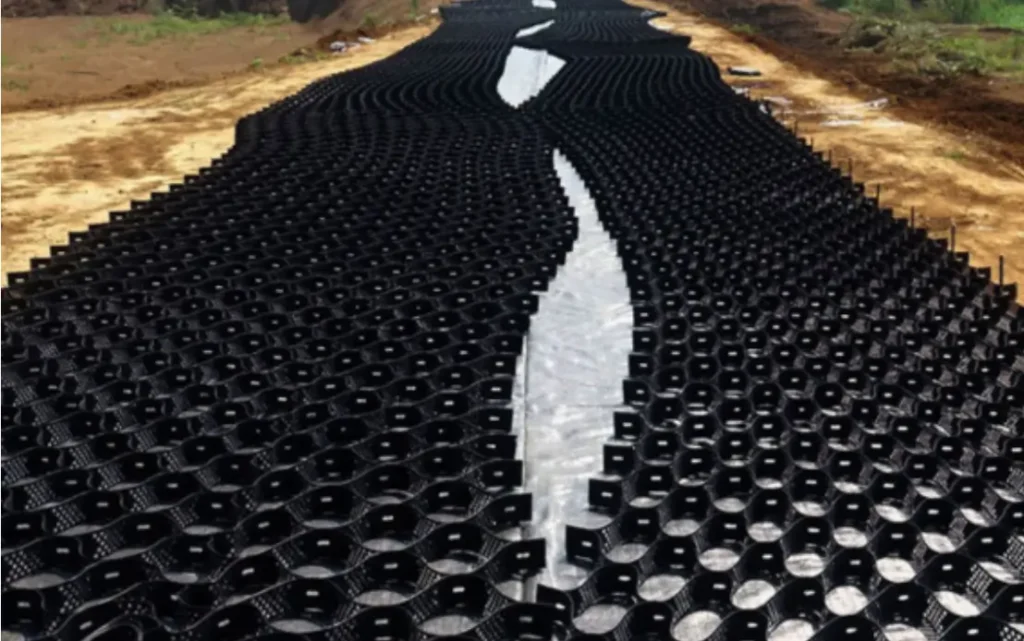
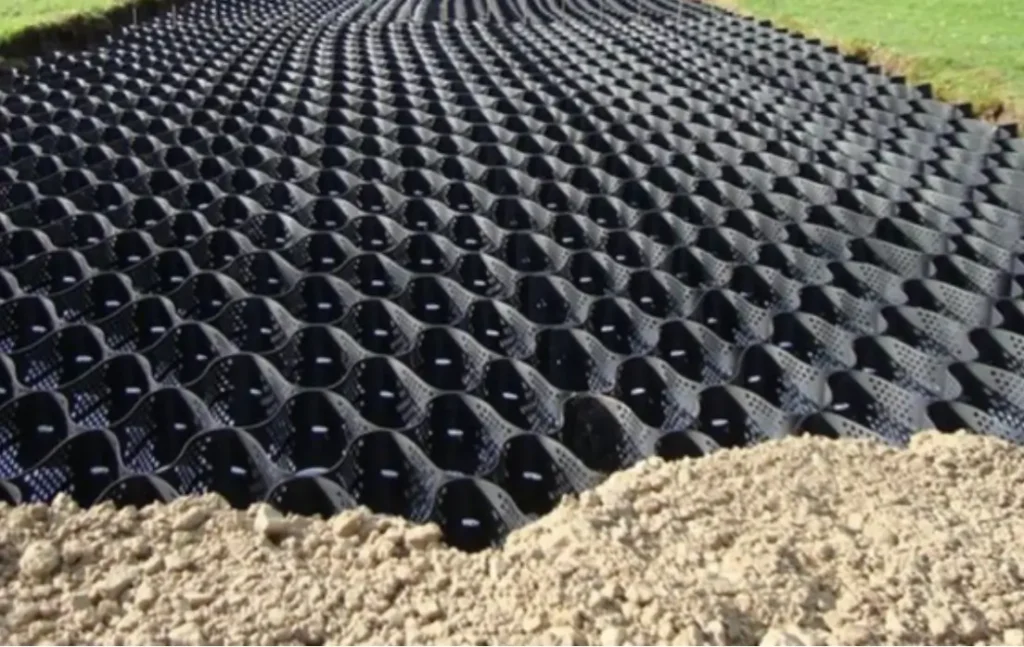


The main purpose of geocell ground grids is to ensure that soil is protected and stabilized. They increase the efficacy of standard civil building and erosion prevention materials.
The materials are 3D, expandable panels fabricated using polymeric materials. When you expand them during geocell installation, the intertwined strips develop the walls of elastic, 3D cellular structures. It is in these structures that you place and compact the stipulated infill materials.
Consequently, the expansion forms a free-draining system, which locks up the infill substances in place. It also inhibits mass displacement by offering confinement via tensile reinforcement. The operational and structural properties of infills and topsoil are strengthened by the geocell confinement system.
The selection of infill material is basically dictated by the intensity and nature of expected working strains. You should also consider the cost and availability of candidate materials, and the aesthetic necessity for a completely vegetated look. prevalent geocell filler products include concrete, aggregates, and cultivated surface soil.
Difference Between Geogrid and Geocell
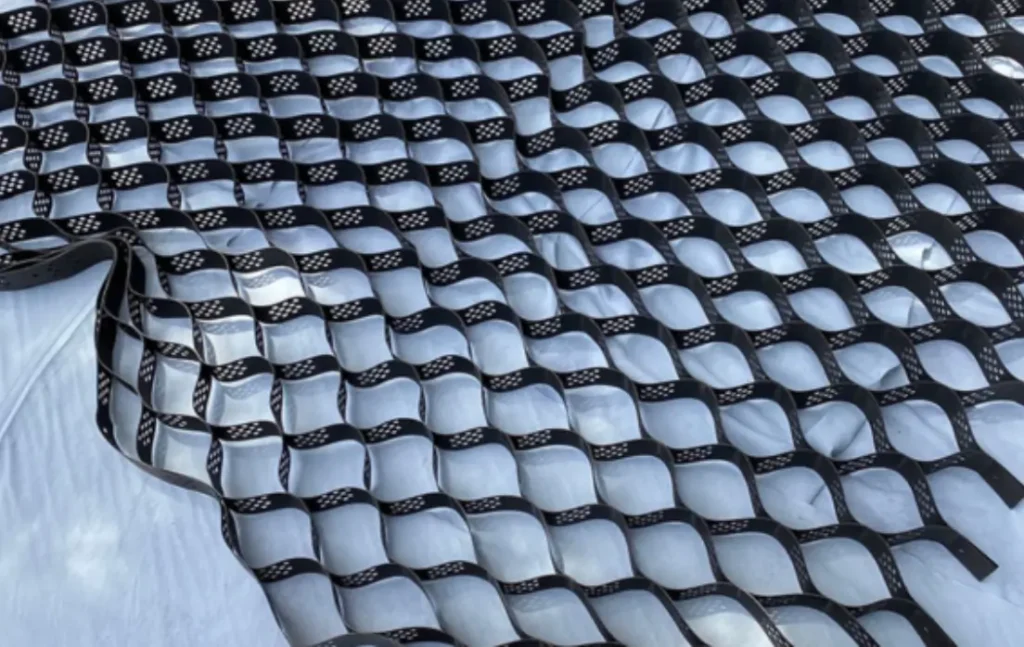
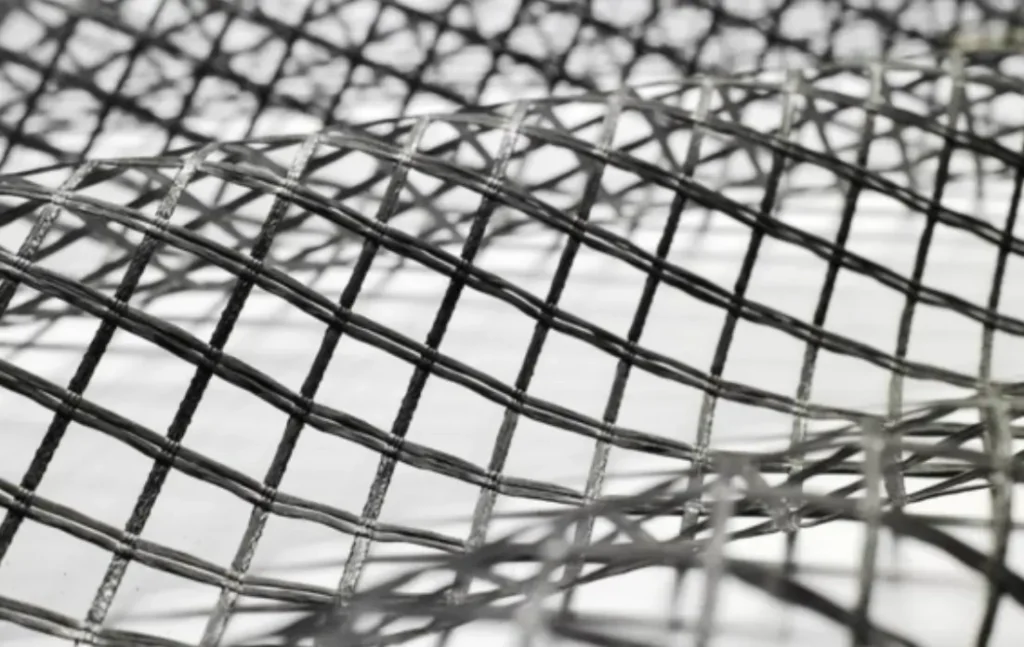


When it comes to geotechnical applications several materials and techniques are utilized to improve soil stability and for reinforcement. The table below shows the geogrid vs geocell comparison:
| Comparison | Geogrid | Geocell |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Geogrid are grid-like structures made of interconnected ribs and apertures. | Geocells are a three-dimensional cellular structure made from strips. |
| Load bearing capacity | The load bearing capacity of the geogrid is restricted by the flat nature of its surface. | Can sustain and endure more weight. |
| Flexibility | The flat 2D nature of the geogrid allows them to bend to accommodate irregular surfaces. | The 3D nature of the geocell restricts them from bending hence they are less flexible. |
| Costs | The installation of geogrids requires the use of expensive fill materials which makes it more costly in the long run. | Geocells tend to be more cost-effective for applications that require load distribution and confinement, as they can reduce the need for extensive excavation and the use of expensive fill materials. |
Properties of Geocell
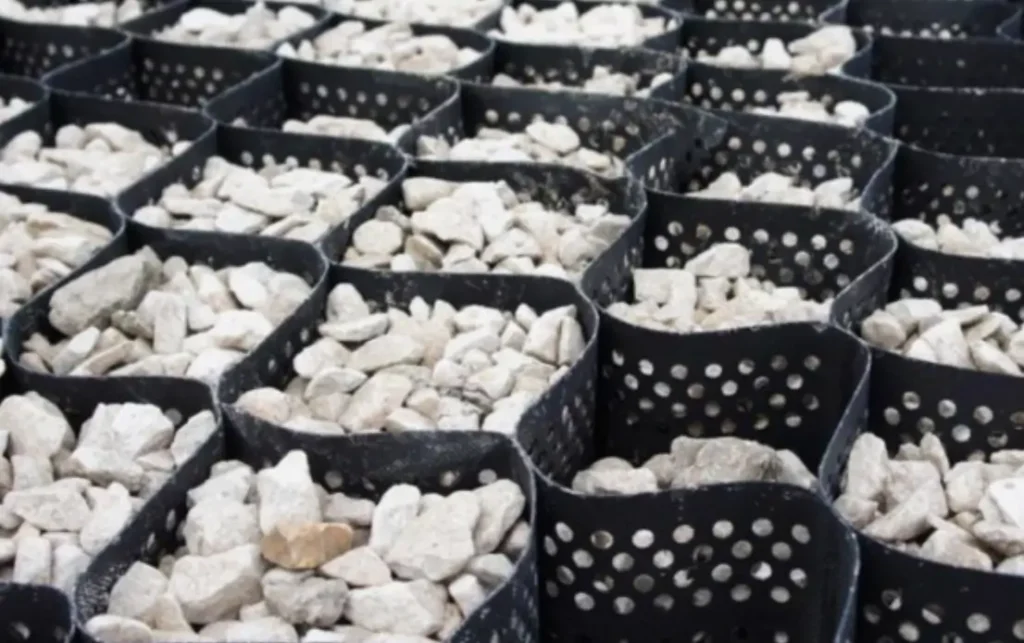
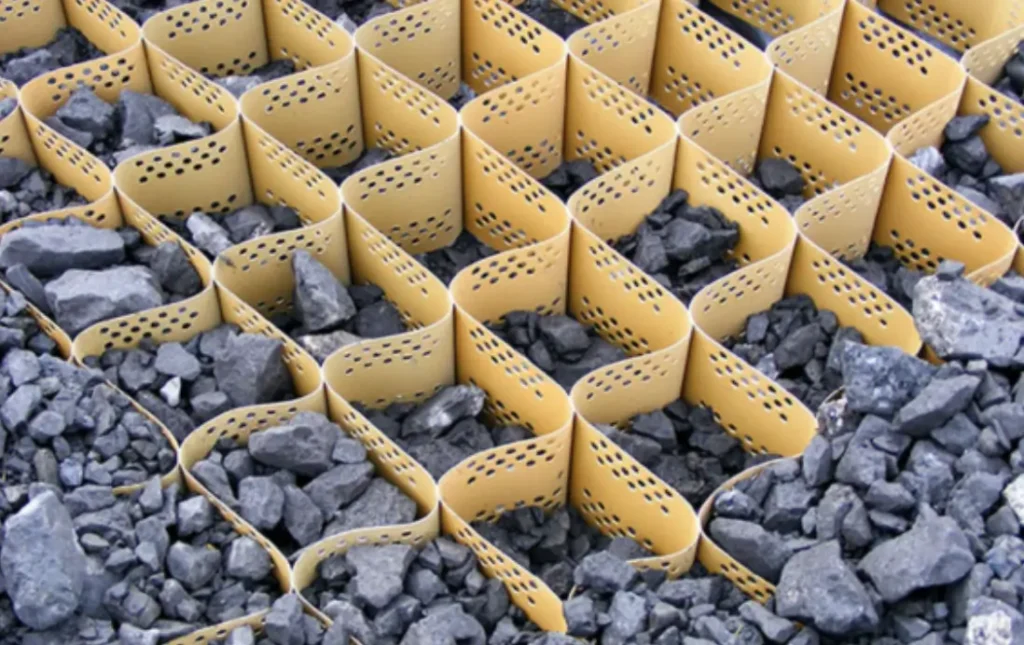


Geocells possess several important properties that make them effective in geotechnical and civil engineering applications. The table below highlights the key features of geocells:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Cellular Structure | Geocell grids constitute interlinked cells or cavities set out in a honeycomb layout. The cells normally have rectangular or square shape, though there are also other patterns. The cell-like framework provides neighboring soil or filler materials with confinement and reinforcement. |
| Mechanical Strength | The polymer materials used in geocell manufacturing have exceptional compressive and tensile strength properties. This enables them to endure heavy loads and guarantee structural stability. |
| Permeability | Geocell products are highly pervious, allowing free flow of water across the cells. This is critical in maintaining soil moisture equilibrium, avoid erosion, and control accumulation of water. |
| UV Stability | The material can endure extended ultraviolet ray exposure without considerable deterioration. The materials used in geocells manufacturing are UV-stabilized, which ensures that the products maintain their performance and structural integrity over the years. |
| Chemical Resistance | Geocells grids have high resistance to a variety of chemicals, consisting of organic solvents, alkalis, and acids. This guarantees their long-term functioning and longevity in conditions susceptible to chemical exposure, like waste containment areas and industrial sites. |
| Weight | Because of their light weight, handling and installation of geocells on-site is very easy. Being lightweight also decreases the general force on the construction and reduces the necessity for equipment for installation. |
| Flexibility | The flexible nature of geocell systems facilitates easy bending and shaping to adjust to irregular terrains or surfaces. Because of this, the cellular confinement systems can adapt to fluctuation in ground elevation and different site settings. |
| Intertwined | Geocell materials feature a distinctive interlocking mechanism that facilitates their interlinking to create a continuous and steady structure. The meshing avoids lateral cells displacement and boosts geocell system stability. |
Applications of Geocells
Road Building
Geocells grids serve to better all-around road performance, limit pavement breakdown, as well as boost load-bearing potential.
Stabilization of Slopes
The geosynthetic systems are effective in soil erosion prevention, minimizing landslides, and giving support, thus boosting slope stability.
Retaining Walls
Geocell systems can be utilized in the construction of retaining walls as they offer reinforcement to the walls and are very flexible. This flexibility allows the geocell to be installed around pipes, irregular structures and curves.
Landscaping and Erosion Mitigation
Using Geocell products to construct green spaces, gardens, and terraces, they help in enhancing the topography aesthetic.
Mining
Geocell materials are applied in mining operations to improve stability, control erosion, and enhance environmental containment. This protects the mine from potential collapse.
Channel Protection
Geocells are commonly used to stabilize and reinforce the banks of channels, rivers, and other water bodies. They offer effective erosion control and enhance the overall stability of the channel hence maintaining the integrity of the watercourse.
Advantages of Geocell
Geocell materials offer numerous benefits to civil engineers including:
· Multi-Purpose and Versatile
Geocell confinement systems are very versatile and can serve many roles, including retaining walls, slope reinforcement, base stabilization, and channel protection. You can easily install and fill them with different materials, such as recycled matter, sand, aggregate, or soil, dependent on the project needs. It is also possible to have customized geocell systems to match irregular contours or shapes, which makes them ideal for difficult terrains.
· Easy Installation
The lightweight and flexible properties of geocells makes handling and installing them very easy. It is possible to unroll and expand the materials to cover broad areas very fast. Normally, connectors or fasteners help in interconnecting and securing the geocell systems to develop a continual and firm structure.
· Load Distribution
The geocell material is capable of distributing the load through a bigger area, this ensures efficient stress reduction on the base soil. The chambers confine the fill or aggregate materials, prohibiting lateral movement and increases the soil’s load-bearing ability. This is specifically vital in geocells for road constructions.
· Durability
Most geocell manufacturers design the cellular confinement systems to survive severe environmental conditions and ensure longer service life. They use top-quality geocell materials that are resistant to chemical, biological and UV degeneration. This sustains the structural integrity of the system through a prolonged duration.
· Cost-Effective
Geocell products are a cost-saving option to conventional construction techniques. The cellular confinement systems reduce material requirements, extensive earthworks, and optimize construction duration. The potential of using on-site fill materials and soils further lower the costs of transportations and ecological impacts.
· Environmental Compatibility
These types of geosynthetic are eco-friendly and consistent with different ecological systems. Geocell grids facilitate vegetation growth, encourage ecological restoration, and blend with nature seamlessly. The products also support sustainable management of water, prevent waterlogging, and promote water drainage.
What are the Disadvantages of Geocells?
Other than there many advantages, there are also several geocell limitations that should be put into consideration:
- Geocells are more expensive compared to the traditional methods of construction in terms of the initial material costs.
- The resin used in geocells manufacturing is not highly durable and needs to be coated with additives to perform efficiently. These additives are necessary to inhibit oxidation and provide protection against UV radiation.
- Specialized tests have to be done to ascertain that the geocells and the infill material chosen suite the soil types and the environment.
- The performance of geocells may be reduced highly by corrosive environments as they are not compatible with all chemicals. Certain acids, alkalis and organic solvent may degrade the integrity of the geocell structure.
- Careful handling during storage, transportation and expert installation is recommended for optimal performance.
How much is Geocell Price?
Costs incurred is a critical consideration when choosing the most appropriate Geocell for your project. The price of geocell is dependent on the manufacturing company, project size, geocell type and the material specifications.
You also have to consider the infill, base clips and base caps that are within your budget. Generally, geocell cost anything between $0.4-$8 for every square meter of material. The most common infills used with geocells cost 0.8$-18$ for every square foot of material.
What is the Depth of Geocell?
The depth of geocell can range from 50mm-300mm depending on the specific project requirements. The depth of geocells directly influences their performance. It is therefore important to select the most appropriate depth for your project.
How do you Determine the Strength of Geocell?
Testing the welded seam strength and tensile strength will help in determining the geocell grid strength. The strength of the welded seam should be the same as or higher than its tensile strength for the material to perform efficiently.
Let us discuss the tests performed on the Geocell:
- Strip tensile strength: This test is done by an extensometer. The test is carried out using a geocell featuring an expansive width because they provide a significant number of apertures from an individual seam to the next.
Loads are applied on the length of the material at a constant rate until the material breaks. The tensile strength and the strain of the maximum load are taken.
The maximum load that should make the material rupture should range between 1kN-m to 25 kN-m for geocells that are non-perforated and 16kN-m to 22 kN-m for perforated geocells.
- Seam weld strength: You perform the test geocell welded seams. It involves apply a force perpendicularly to the point of intersection at a rate of 100 mm/min. This force is increased gradually until the seam yields to it and ruptures.
The seam weld tensile strength is recorded as maximum force applied to make the seam rupture. The minimum seam weld strength should not be less than 16kN/m.
What is the Best Gravel for Geocell?
When selecting gravel for geocell applications, it is important to consider factors such as particle size, compaction and angularity. Generally, well-graded granular materials with angular particles are preferred to ensure effective interlocking and load distribution within the geocell system.
The best gravel for use is the compacting gravel as it prevents the quicksand effect. You are recommended to pick compacting 3/8-inch gravel over the rounded fill and pea gravel.
Can you cut Geocell?
Yes, you can cut geocell. Geocells are manufactured in the form of panels which may have to be cut to desired shapes and dimensions to accommodate your project needs.
To achieve this, you need to use appropriate tools and techniques. You can use sharp knives or heavy-duty scissors can be used to make clean and precise cuts. However, it is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and recommendations to ensure that the geocell does not lose its integrity.
One Stop Geosynthetics Manufactry Leader
Lianyi is a trusted geosynthetic manufacturer for over 10 years with our expertise and vast knowledge in the industry.
