Puddles ruin lawns. Tires sink. You want clean parking that still looks green. Is there a simple way to carry cars and keep grass alive? You’ve heard of HDPE grass paver? Let’s walk through it in plain language.
HDPE grass pavers are interlocking plastic grids that spread wheel loads while letting rain soak into the soil. They protect roots, stop ruts, and create strong, permeable surfaces for cars, fire lanes, and footpaths.
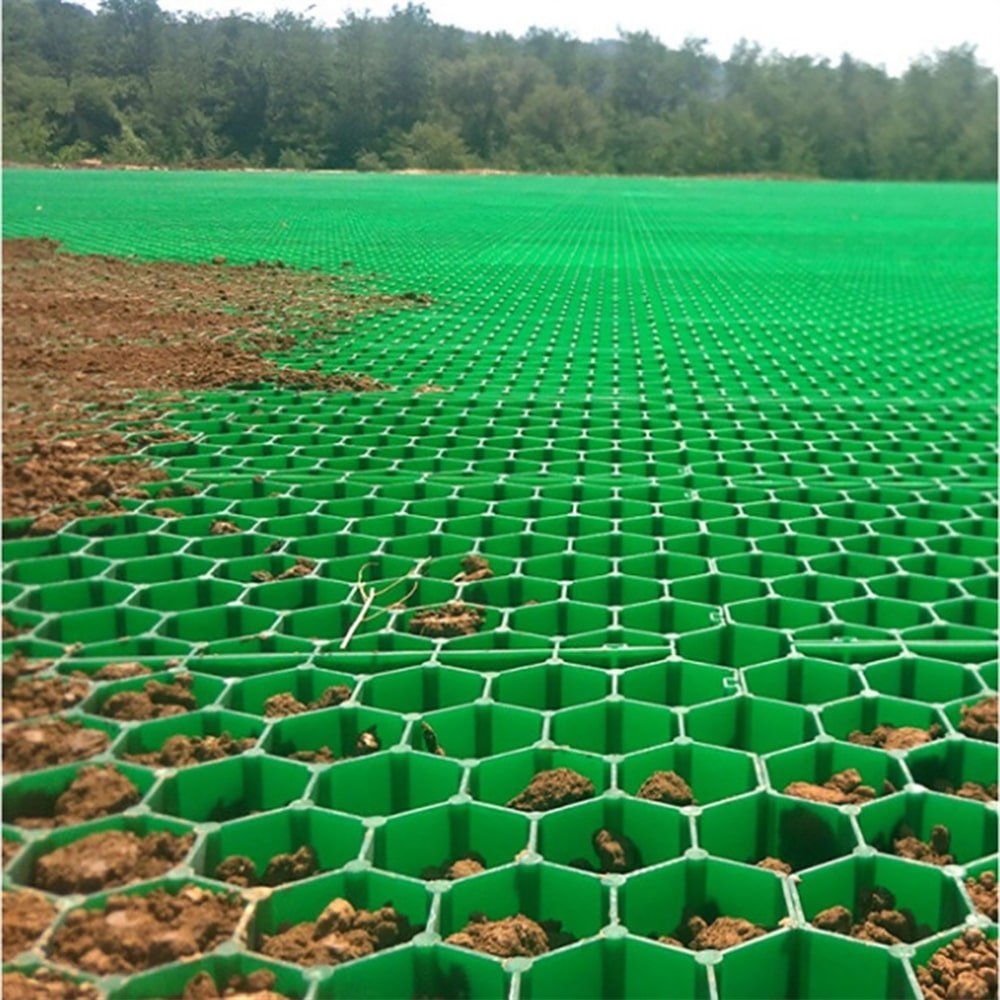
Many buyers compare plastic grids, concrete grass blocks, and gravel stabilizers. The names sound similar. I will break down what HDPE grass pavers are, what they do, how they are made, where they fit, the pros and cons, types, comparisons, and practical steps for design, installation, and care.
What is HDPE grass paver?
Bumpy turf and soft subgrade do not carry loads. Wheels punch through. Maintenance never ends. A stable, green surface fixes this.
Defination
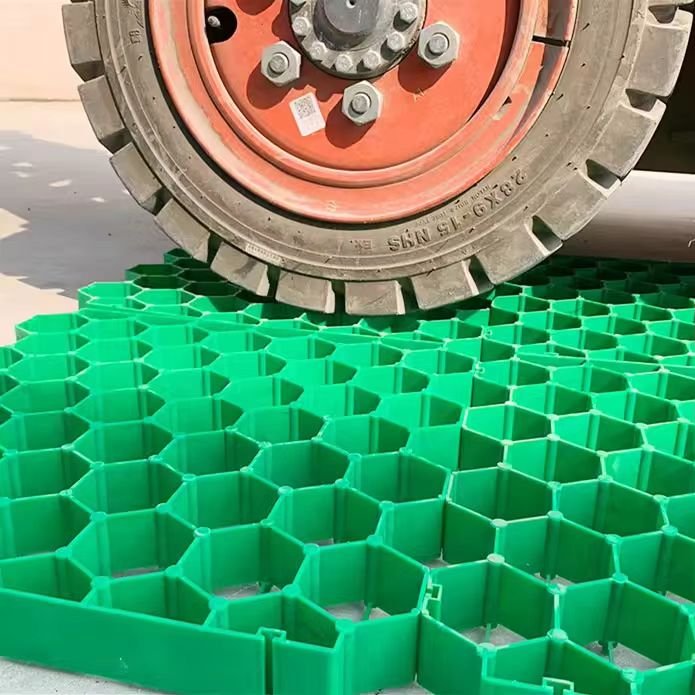
An HDPE grass paver is a modular, open-cell grid molded from high-density polyethylene. Cells accept soil and seed or a soil–sand mix. The grid spreads load, protects roots, and lets water infiltrate. Panels lock together and sit over a prepared base with drainage.
Let me unpack the material and the product form. HDPE means high-density polyethylene. It is a tough, ductile thermoplastic. It resists water, salts, and many chemicals. It has good impact strength at room temperature. It also supports UV stabilization with carbon black or light stabilizers. In grass pavers, HDPE gives a sweet spot between stiffness and toughness. It flexes a little under load to share stress, but it does not crack like brittle plastics.
What is an HDPE grass paver made of?
Producers compound HDPE pellets with 2–3% carbon black or HALS (hindered amine light stabilizers), antioxidants for heat, and sometimes pigments. Many factories include a portion of recycled HDPE if the spec allows. The process is injection molding. Pellets melt in a barrel. The melt fills a steel tool that forms the honeycomb or lattice. After cooling, ejector pins push out the tile. Trimming and visual checks follow. Each tile has male–female clips or tabs for quick interlock on site. Wall thickness, cell height, and rib geometry set the load rating. Rib feet or anchors add grip on the base. Some models include integrated geotextile on the underside to keep fines from moving up.
What do these tiles do in service? The cells confine the root zone and the infill. Confinement stops lateral spread and rutting. It also reduces contact pressure on the subgrade. Wheels ride on many ribs at once, not on one spot. Water drains through the open area, so you avoid ponding. Roots grow down through the openings. This supports turf health when traffic is light to moderate. With the right base and turf care, the surface stays green and firm.

What are HDPE grass pavers used for?
You need one system that handles people, cars, or light trucks, and still meets drainage goals. You also want easy logistics.
HDPE grass pavers support overflow parking, fire access lanes, emergency shoulders, golf paths, RV pads, event lawns, tree root protection near structures, and low-speed residential driveways. They work where stormwater rules push permeable paving.
1. Think in use cases. Overflow parking at schools, event centers, or parks needs green space most days and hardstanding on peak days. A grass paver turns a lawn into a structural surface that accepts cars without turning to mud. Fire lanes must support vehicle loads, but do not need asphalt aesthetics. Grids provide the rated bearing and stay discreet under turf. Tree root protection zones near heritage trees cannot take heavy compaction. Grids spread the load over a wider area, so the root zone breathes. Paths for golf carts and maintenance vehicles benefit as well; the grid keeps edge lines neat and reduces scalping on turns. Residential driveways and RV pads use grids to meet local permeability targets and to reduce the heat island effect. In cold regions, grids also help with shoulder stabilization where snow pushes traffic onto grass.
2. Let me map these needs to basic design choices. For cars and pickups, a cell height of about 40–50 mm with a compacted granular base works in many cases. For light fire access, thicker ribs and tested load data matter; follow the authority having jurisdiction for loading. For event lawns, fast installation and soft aesthetics drive the pick; quick-lock tiles help crews. For root protection, choose a model with a high void ratio and avoid fines in the root zone. For slopes up to a gentle grade, grids can hold turf, but steep slopes need extra anchoring and careful irrigation. The common thread is load sharing plus permeability. If you pair grids with a good base and grass species fit for traffic, you will get a surface that earns its keep.

Pros and cons of HDPE grass paver?
Every product has trade-offs. It helps to see both sides before you place a PO.
Pros include permeability, green look, light logistics, fast setup, and flexible layouts around trees and curves. Cons include turf maintenance, snowplow care, base prep needs, and limits under tight turning by heavy trucks.
Dive deeper
Pros first. Permeability is the standout. Rain enters the ground where it falls. This can reduce stormwater fees and ponding. The green surface cuts heat buildup compared with asphalt or concrete. Logistics are light; tiles stack tightly and carry by hand. Interlocking patterns make curves and edges simple. Repairs are local; you can lift one panel and fix a soft spot. Noise is low, and appearance blends with landscape design. HDPE also resists many de-icing salts and hydrocarbons, which supports long service in parking contexts.
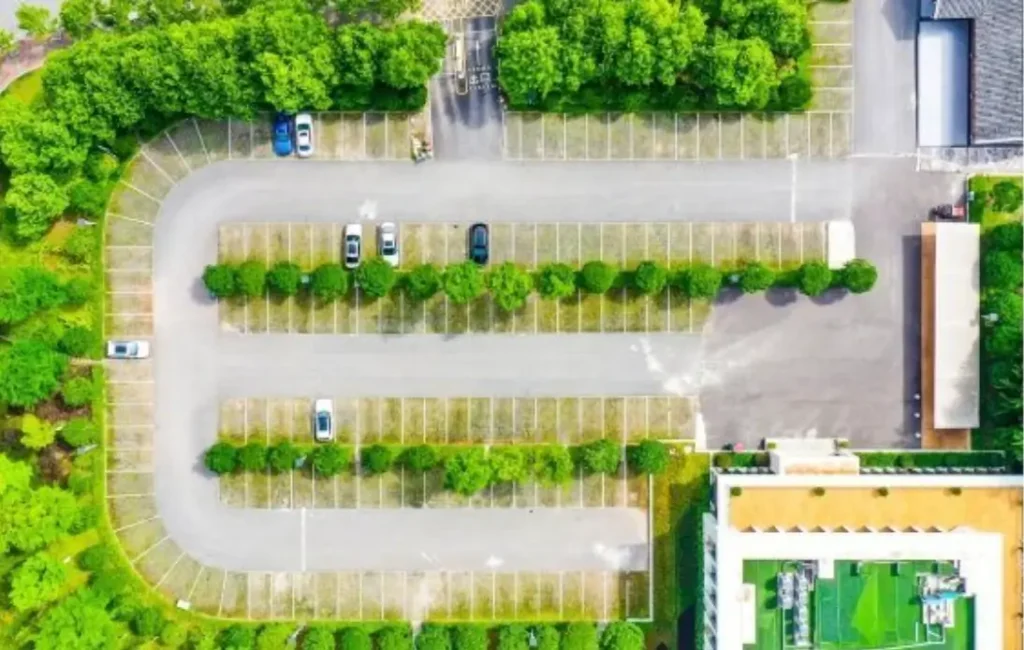

Now the challenges. Turf is a living system. It needs species selection, soil mix, irrigation, and mowing plans. In shade, grass thins. In drought, it goes dormant. You avoid most of this with the right seed mix and realistic traffic plans. Base preparation matters. If you install grids on soft soil with no base or separator, you will see undulations and ruts. Turning shear from heavy trucks can scuff turf, especially in hot weather. You handle this with turning aprons of gravel, pavers, or concrete at known turn spots. Snowplows can catch ribs if blades run too low. Operators need a rubber edge or skids set a bit high. UV exposure is another factor for empty grids before fill. Store covered and backfill soon after placement.
Here is a quick view you can share with teams:
| Factor | Pro | Con | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stormwater | Infiltration | None | Verify subbase storage capacity |
| Aesthetics | Green, cool | Seasonal color change | Select hardy turf, overseed |
| Structure | Load sharing | Needs base | Proper subgrade and base design |
| O&M | Local repairs | Turf care | Seasonal plan, traffic control |
| Winter | Ice melts through | Plow risk | Skid shoes, rubber edge |
What are the types of HDPE grass pavers?
Choice can feel endless. A clear map speeds ordering and reduces RFIs.
Types differ by cell height, wall thickness, open area, connection style, underside features, and intended infill. Some models suit grass. Others suit gravel. Some do both with minor changes to the base and fill.
Dive deeper
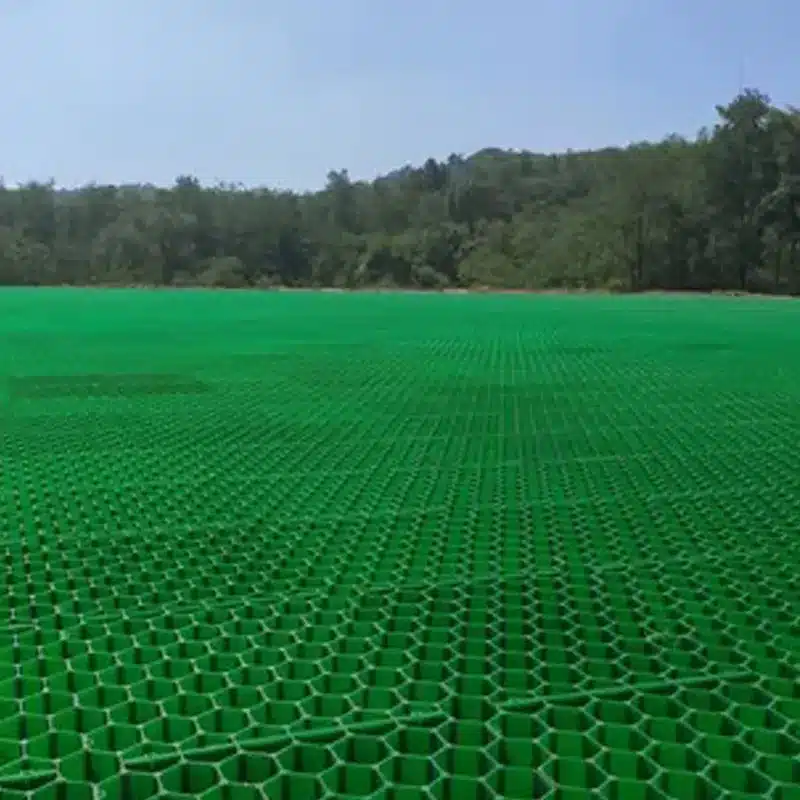
Let me group the market in a simple way. Cell height often ranges from 30 mm to 60 mm. Short cells aim at pedestrian zones and light cars. Taller cells handle higher point loads and protect roots better. Wall thickness and rib design drive the compressive performance and creep resistance. Look for continuous load ribs, cross-ties, and foot pads that spread stress into the base. Open area matters for turf health. High void ratios help grass and infiltration but lower rib area. The best designs balance both.
Connection style affects speed and stability. Snap-fit clips are fast and give audible feedback. Hook-and-eye tabs allow thermal movement. Pin-and-hole designs accept landscape staples for extra hold. Some models ship with geotextile pre-bonded to the underside to limit fines moving up; this helps over weak subgrades. Others have integrated expansion joints to handle heat. For infill, there are grass-only grids with soil mix guidance and gravel/grass hybrids with a chamfered rim that hides stone. Color is usually black or green. Black hides soil and gives better UV screen from carbon black. Green blends with turf but needs an extra light stabilizer.
You can also classify by base design intent. Turf-focused systems use a root zone mix (sand with compost), irrigation lines, and seed or sod. Gravel-focused systems use angular stone graded to lock in place and drain. Both can use the same tile if the rib geometry and wall height are sufficient. For steep drive strips or fire lanes, select models with published load and creep data at realistic temperatures. This avoids surprises after a hot summer.

Is HDPE grass paver better than other kinds grass paver?
You will see PP plastic grids, concrete grass pavers, and even geocell panels pitched for the same job. Which one makes sense?
HDPE grass pavers beat PP in toughness and low-temperature impact for many climates. They beat concrete blocks on weight, logistics, permeability continuity, and root protection. Geocell can work for slopes and soft bases, but it is not a finished wearing surface. The right choice depends on load, climate, and maintenance plans.
Dive deeper
Let me compare with a simple decision lens. Against PP grids, HDPE has better ductility and stress-crack resistance. PP can be stiffer at room temperature, but it can also be more brittle in cold snaps. If your site sees freeze–thaw and impacts from light trucks, HDPE’s toughness pays back. Against concrete grass pavers, the story is different. Concrete units offer high compressive strength and a rigid plane. They work under tighter turning loads. They also carry high heat mass and less void area. They weigh a lot, which increases handling costs and slows work. Concrete also reflects heat and may stress turf in hot climates. HDPE tiles are light, fast to place, and keep more active root volume. For fire access with strict code loads and high turning, a concrete or hybrid section near corners can still make sense. For most overflow parking and driveways, HDPE gives a better balance of performance, speed, and vegetation health.
Now geocell. A geocell is a deep cellular confinement made from HDPE strips welded into honeycomb panels. It is great for stabilizing soft subgrades and slopes. It is not a wearing course by itself. If you fill geocell with soil on a driveway, tires will peel the surface unless you cap it. If you fill with gravel, you lose the grass goal. So, many teams use geocell under a thin base to stiffen weak soils, then place grass pavers above. This pairing handles very soft ground, reduces base thickness, and keeps the green surface. The point is simple: choose the system by function. For a finished, permeable, green driving surface, HDPE grass pavers are usually the better fit.
How to install HDPE grass paver?
Good tiles fail on bad bases. Good bases shine with simple, repeatable steps.
Set grades, build a draining base, place a separator if needed, interlock tiles, fill with root-zone mix, seed or sod, water, and protect during establishment. Small details drive the result.
Dive deeper
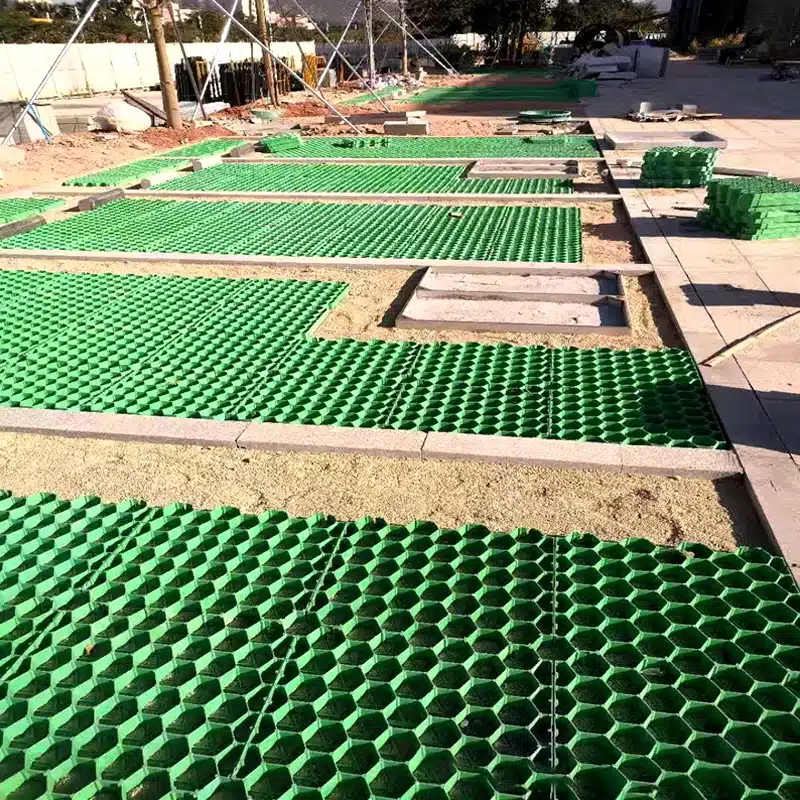
I will outline a clean sequence you can hand to crews. First, subgrade. Proof-roll the area. Cut out soft spots. Replace with compacted granular fill. Aim for uniform support. Install edge restraints where the grid meets pavements or planting areas. Second, base. Use a well-graded, free-draining aggregate. Thickness depends on load and soil; light cars on firm soils may need 100–150 mm; softer soils or frequent loads may need more. Compact in thin lifts to target density. If the native soil is fine or wet, place a nonwoven geotextile separator between the subgrade and base to prevent pumping.
Third, bedding. Place a thin bedding layer, often 20–30 mm of sand or sand–soil blend for turf systems. Screed it flat. Fourth, tiles. Start from a straight edge. Snap tiles together in the direction of travel to avoid lifting the previous row. Keep joints tight. Cut with a saw at curves and edges. Use landscape staples or pins where the spec calls for extra hold, such as slopes. Fifth, infill. For grass, use a root-zone mix with sand dominance for drainage and shear strength. Brush the mix into cells and lightly compact to remove voids. Do not overfill well above the cells; you want the turf to sit flush after growth. Sixth, seed or sod. For seed, choose a wear-tolerant mix for your climate. For sod, pick a species grown on sandy soil to match the root zone. Seventh, water and protect. Irrigate to keep the root zone moist during establishment. Keep vehicles off until turf roots bond. Mark the area with temporary posts if needed.
Snow regions need one extra step: brief the plow operator. Set blades a little high or use rubber edges. Place turning aprons of gravel or concrete in tight corners where drivers will scrub the surface. These small notes prevent seasonal damage.

How to choose and specify HDPE grass paver?
Many catalogs look similar on paper. A short, testable spec protects your project and keeps bids fair.
Match load rating to use, pick cell height for root zone and protection, check UV and creep data, plan the base and edge details, and write the infill and turf mix into the PO. Clear data avoids change orders.
Dive deeper
Start with use and traffic. For overflow car parking and driveways, ask for published compressive strength and creep data at realistic temperatures. Confirm test methods. For fire lanes, align with the authority load case and subbase design. Set cell height and wall geometry. Heights of 40–50 mm are common for vehicles. Thicker ribs help with long-term creep under parked loads in hot weather. Check UV package. Carbon black is the simplest and most robust solution for black tiles. For green tiles, ask for HALS data. Review connection style and thermal movement allowance, especially in hot climates.
Now the ground system. Specify subgrade improvement, separator geotextile if needed, base gradation, base thickness, bedding layer, and edge restraints. Write the root-zone mix recipe: sand percentage, organic content, and particle size. Name the seed or sod mix by species and rate. Add a short O&M note: irrigation during establishment, mowing height, and seasonal overseeding. These lines cost little and prevent disputes.
Here is a compact checklist you can paste into a tender:
| Item | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material | HDPE with UV stabilizers; carbon black for black color |
| Cell height | 40–50 mm for vehicles (project to confirm) |
| Wall thickness | Provide nominal and tolerance; rib design shown |
| Open area | State percent void for infiltration and turf health |
| Interlock | Snap-fit or tab system; thermal movement allowance |
| Tests | Compressive strength and creep at service temperature; impact; UV retention |
| Base | Granular gradation and thickness per soil and load |
| Infill | Root-zone mix spec; seed/sod type and rate |
| Edges | Restraints at pavements and soft edges |
| O&M | Establishment irrigation; mowing; snowplow guidance |
My opinion
I usually suggest choosing by function, not by brochure photos. If the goal is green, drivable, and permeable, HDPE grass pavers hit the mark on most sites. Put your effort into the base, the root-zone mix, and turf care. Add turning aprons where drivers will scrub. Keep the spec short and measurable, and the job will go smoothly.

FAQ
What is HDPE?
High-density polyethylene. A tough plastic with low water uptake, good chemical resistance, and good impact strength.
Can HDPE grass pavers handle fire trucks?
Some models can, with the right base. Ask for tested load and creep data and follow local fire lane standards.
Do grids work with gravel instead of grass?
Yes. Many tiles take gravel infill for low-maintenance permeable parking. Use angular stone and a geotextile separator.
How tall should the cells be?
For cars, 40–50 mm works on a proper base. For heavier loads or root protection, taller cells can help.
What base do I need under the grids?
A compacted, free-draining granular base. Thickness depends on soil and load. Include a separator geotextile over fine or wet subgrade.
Will the grass die under cars?
Turf survives if you select hardy species, use a sandy root zone, irrigate during establishment, and manage traffic. Shade and drought reduce performance.
How do I plow snow on a grid lawn?
Use a rubber edge or set blades slightly high. Avoid aggressive scraping. Mark edges before winter.
What about UV aging?
HDPE with carbon black shows strong UV resistance. Store tiles out of sun before install and fill soon after placement.
Are green tiles better than black?
Color is visual. UV package matters more. Black has carbon black, which is robust. Green needs HALS. Ask for data.
Can I use geocell instead of grass pavers?
Use a geocell to stiffen soft subgrades or hold slopes. It is not a finished wearing surface for grass driveways without a cap.
How do I estimate quantity?
Divide the area by the coverage per tile, add 3–5% for cuts and waste, and include edge restraints and pins where needed.
What maintenance is required?
Normal turf care: mowing, irrigation in dry spells, seasonal fertilization or overseeding, and quick repair of damaged spots.
How long do HDPE grass pavers last?
With proper base, UV stabilization, and normal service, service life is long. Many systems run for years with routine turf care.
Conclusion
HDPE grass pavers turn soft lawns into strong, permeable parking and paths. Match tile type to load, build a proper base, choose the right root zone and turf, and your green surface will stay firm and clean.
MJY Geosynthetics Manufacturer has been dedicated to producing high-quality geosynthetic materials for 15 years and is a recognized leader in the industry. If you are interested in finding a reliable one-stop geosynthetics supplier for your project or business, please visit our website for more information:





