What is a biaxial geogrid?
Biaxial geogrids are a popular choice for soil stabilization thanks to their strong, reliable performance in two directions. Made from punched-and-drawn polypropylene or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), these geogrids feature square or rectangular apertures. This design provides equal tensile strength along both the machine and cross-machine directions, making them ideal for predictable load paths.
Core Structure and Manufacturing
- Material: Polypropylene or HDPE
- Apertures: Square or rectangular, ensuring uniform strength
- Process: Manufactured through extrusion, precise punching, and orientation
- Result: Strong, rigid junctions that enhance aggregate interlock and overall stability
Performance Advantages
Biaxial geogrids excel at lateral confinement within straightforward stress fields. Independent studies show they can reduce rutting in flexible pavements by 30-40%, which translates to longer-lasting roads with less maintenance.
Limitations to Consider
While great under bidirectional loads, biaxial geogrids perform less effectively under multi-directional shear stresses, such as those occurring at 45° angles. This can lead to higher aggregate requirements in complex load environments where forces come from various directions.
MJY Spotlight: BX-Series Biaxial Geogrids
MJY’s BX-series biaxial geogrids meet stringent AASHTO standards, making them a trusted solution in the U.S. market. For example, a recent highway project in the Midwest reduced pavement base thickness by 25%, proving both performance and cost savings with MJY’s product.
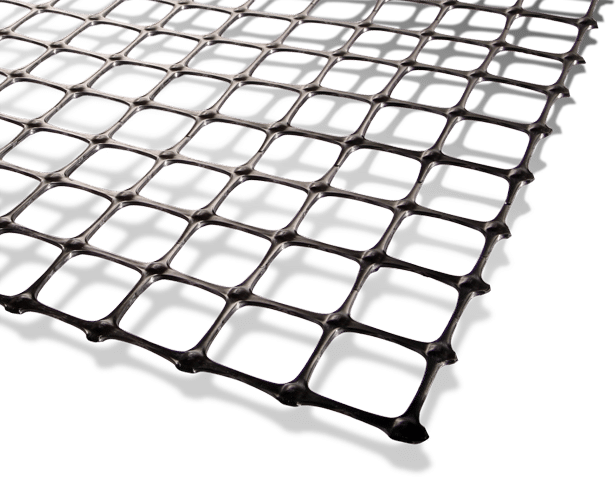
What is a Triaxial geogrid?
Triaxial geogrids stand out with their unique triangular apertures and multi-rib design, providing strong reinforcement in multiple directions. Unlike biaxial geogrids, they distribute loads evenly across three axes—radial, circumferential, and tangential—making them ideal for projects where forces come from various angles.
These geogrids are made using an advanced extrusion process that creates ribs with higher aspect ratios (around 1.5:1). This method, developed in the late 2000s, enhances the strength of the junctions where ribs meet, boosting durability and load distribution.
Performance-wise, triaxial geogrids offer up to 50% better aggregate confinement, especially in high-traffic areas like highways and airports. Their uniform tensile strength, often between 25-50 kN/m, helps reduce deformation under dynamic or shifting loads—a fact supported by field tests from Montana State University.
However, triaxial geogrids come with some drawbacks. They tend to cost more upfront, and their narrower ribs require more careful installation. Some European studies have found that triaxial grids don’t always outperform biaxial options in simpler setups.
At MJY, our TX-series triaxial geogrids are designed with these challenges in mind, optimized specifically for demanding projects like airport runways. For example, during a major port expansion in Asia, using our TX-series cut maintenance needs by 35%, proving its value in real-world applications.
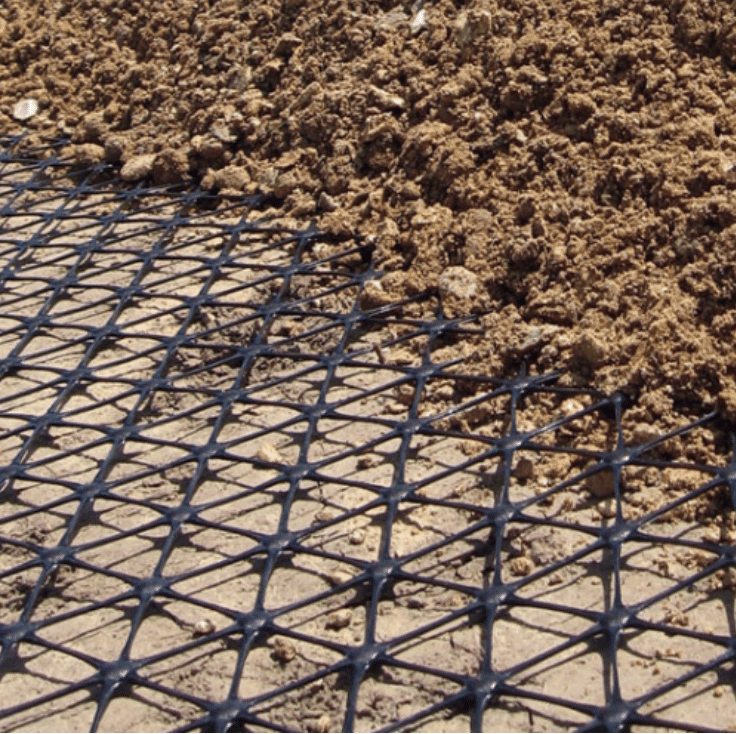

Biaxial Geogrid vs Triaxial Geogrid Performance
Here’s a clear side-by-side look at biaxial and triaxial geogrids so you can see how they stack up on important factors:
| Feature | Biaxial Geogrid | Triaxial Geogrid |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Geometry | Square apertures for strong bidirectional support | Triangular apertures for multi-directional interlock |
| Load Bearing | Best for uniaxial/biaxial loads (retaining walls, pavement bases) | Excels under omnidirectional stress (haul roads, airports) |
| Durability | Strong UV and chemical resistance | Same, with 20% higher fatigue resistance thanks to rib design |
| Cost | About 15-20% cheaper for typical jobs | Higher upfront cost but saves 10-15% aggregate in optimized designs |
| Environmental Impact | Fully recyclable | Also recyclable, with less material needed—better for green projects |
- Biaxial geogrids work great in straightforward, bidirectional load situations. They’re a cost-effective choice for most roadway and retaining wall projects.
- Triaxial geogrids handle complex, multidirectional loads better. They’re ideal when you need top-level soil confinement and long-term durability, like for heavy traffic or seismic zones.
Use this guide to match your project scope with the right geogrid type and get the most out of your soil stabilization efforts.
Real-World Applications: Matching Geogrids to Project Needs
When choosing between biaxial and triaxial geogrids, it really depends on the specific demands of your project. Here’s how they stack up in common U.S. construction scenarios:
- Road and Pavement Reinforcement:Use biaxial geogrids for cost-effective subgrade stabilization on typical roads. They handle straightforward load directions well and help reduce pavement rutting. For heavy-load highways or freight corridors where cracking under complex stress is a concern, triaxial geogrids are better suited thanks to their multi-directional strength.
- Retaining Walls and Slopes:If your project focuses on vertical soil reinforcement, like retaining walls or steep slopes, biaxial geogrids provide strong vertical pull resistance. For seismic zones or sites with unpredictable stress from multiple directions, triaxial geogrids offer superior multi-axis reinforcement to improve overall stability.
- Railways and Airports:Rail beds and airport runways face constant, multidirectional vibrations from heavy traffic. Here, triaxial geogrids shine by stabilizing ballast and reducing deformation, which prolongs service life and lowers maintenance costs.
- Emerging Uses:In erosion control for embankments and mining haul roads, biaxial geogrids often provide a budget-friendly option, balancing performance with cost efficiency.

MJY Case Studies in Action
- In the Midwest U.S., MJY’s biaxial geogrid was used in a rail upgrade project that boosted load capacity by 40%, offering a reliable yet affordable solution.
- Meanwhile, MJY’s triaxial geogrid played a crucial role in a major Middle East airport runway expansion, where it enhanced safety by handling extreme temperature fluctuations and heavy traffic.
How to Decide: Soil Type, Traffic, and Budget
Choosing the right geogrid boils down to three main factors:
- Soil Conditions: Poor or soft soils with multi-directional stress favor triaxial.
- Traffic Volume: Heavy, dynamic loads lean toward triaxial for better durability.
- Budget: For simpler projects, biaxial often delivers the best value.
MJY provides a helpful flowchart to guide your selection, ensuring your project gets the right geogrid for long-lasting performance.
Installation Best Practices: Ensuring Optimal Geogrid Performance
Proper installation is key to getting the most out of your biaxial or triaxial geogrids. Here’s what you need to know:
Site Preparation
- Compact subgrade to 95% Proctor density for a solid base.
- Avoid sharp aggregates that can cut or damage the geogrid ribs.
Placement Techniques
- Overlap seams by 300-500 mm to maintain strength across panels.
- Use pins or stakes on slopes to keep the geogrid in place during backfill.
- Note that biaxial geogrids have wider ribs, making them easier to handle, while triaxial geogrids require more precise alignment due to their narrower ribs.
Common Pitfalls
- Over-tensioning can cause the grid to creep or deform over time.
- Excess moisture during backfill may reduce aggregate interlock, lowering performance.
- MJY’s geogrids come with durable coatings that help resist damage from moisture and handling.
Quality Assurance
- Follow ASTM D6637 tensile testing standards to verify product strength on-site.
- MJY offers on-site installation support to ensure compliance and best results.
Pro Tip
- For soft soils, consider combining geogrids with geotextiles to create hybrid systems that improve soil stabilization and performance.
Using these best practices helps extend the life and effectiveness of your geogrid installation, saving time and costs on future repairs.
Why Partner with MJY: Your Reliable Source for Premium Geogrids
MJY brings over 15 years of experience as a trusted geosynthetics manufacturer, proudly operating with ISO-certified production and a robust global supply chain. We understand the unique demands of U.S. infrastructure projects and deliver consistent quality every time.
Our product range covers both customizable biaxial and triaxial geogrids, available in rolls up to 6 meters wide. Every product comes with a 20-year warranty, ensuring long-lasting performance whether you’re reinforcing roads, retaining walls, or railways.
Beyond quality materials, MJY offers free design consultations to tailor solutions to your specific project. We also provide rapid prototyping for fast turnaround and hold sustainability certifications to support greener building goals.
Ready to boost your next project with reliable geogrid reinforcement? Contact MJY today for a project-specific quote and experience the difference of proven performance and expert support.





