How to Use Geogrid?
If you’re building a driveway on soft subgrade, holding a hillside, or designing a geogrid fabric retaining wall, geogrid turns marginal ground into reliable structure. This guide shows exactly how to use geogrid—what it is, where it works best, how to install it, how to choose geogrid rolls, and how to think about the cost of geogrid on a bid.
What Is Polyester Geogrid?
Polyester geogrid is a high-tensile reinforcement made from PET yarns, oriented in one or two directions and coated (often PVC or bitumen) for durability and soil interaction. In pavements, slopes, and walls it adds tensile capacity so your soil can act like a composite.
Core options you’ll specify:
- Uniaxial vs. Biaxial:
- Uniaxial (strong in machine direction) for retaining walls and steepened slopes where you need long anchorage lengths.
- Biaxial (balanced strength in both directions) for driveway and pavement bases where traffic loads spread in 2D.
- Construction method:
- Polyester woven geogrids / woven polyester geogrids (interlaced yarns) deliver high tensile modulus and low creep—ideal for permanent soil structures.
- Warp-knit PET and coated PET variants are also common; match aperture size to your aggregate for interlock.
- Durability envelope:
- PET handles long-term loads well. Specify coating for chemical/UV exposure, pH range, and construction survivability.
Where PET geogrid shines:
- Geogrid for driveway and road base stiffening over weak subgrade
- Geogrid slope stabilization and geogrid for hillside protection
- Geogrid fabric retaining wall systems (MSE walls & reinforced soil slopes)
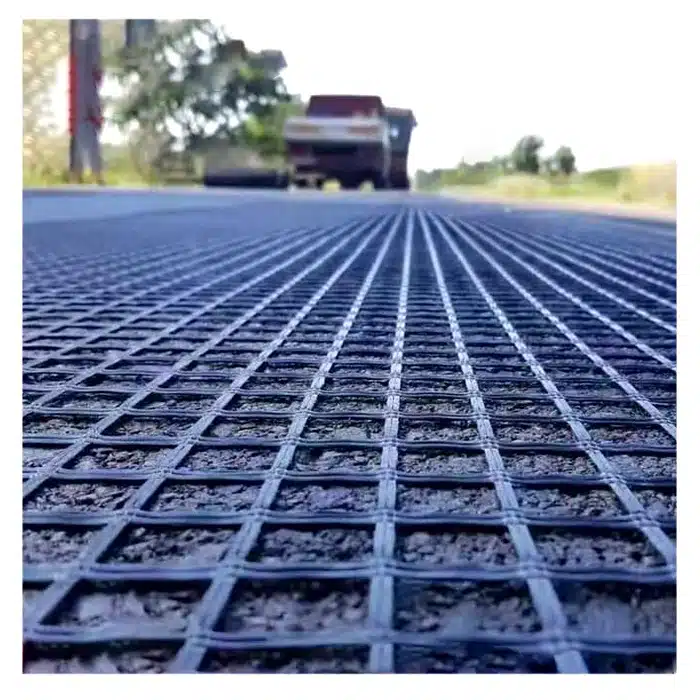
How to Use Geogrid for Driveways & Pavement Bases
Objective: build a stiff, rut-resistant base with less aggregate.
Step-by-step:
- Subgrade prep
- Proof-roll; undercut pumpy spots. Grade to plan. Lay a separation geotextile if fines migration is a risk.
- Geogrid placement
- Roll out geogrid roll perpendicular to traffic direction for better load distribution. Keep it taut and flat—no wrinkles or fishmouths.
- Overlaps: 12–24 in (300–600 mm) typical; increase on very soft ground. Stagger panel ends.
- Initial lift (working platform)
- Place well-graded aggregate (not clayey fines) directly on the geogrid—no tracking on bare grid. Use low ground-pressure equipment to avoid displacement.
- Build to thickness
- Place and compact in 6–8 in (150–200 mm) lifts. Maintain moisture control for density.
- Verify that aggregate particles key through the apertures for interlock.
- Finish
- Shape and cap per design (gravel, asphalt, or pavers). Document densities.
Pro tips:
- Match aperture to aggregate top size (often 1–2× D50) to maximize interlock.
- On peat/silt, a double layer (staggered overlaps) can reduce base thickness and lifecycle cost.

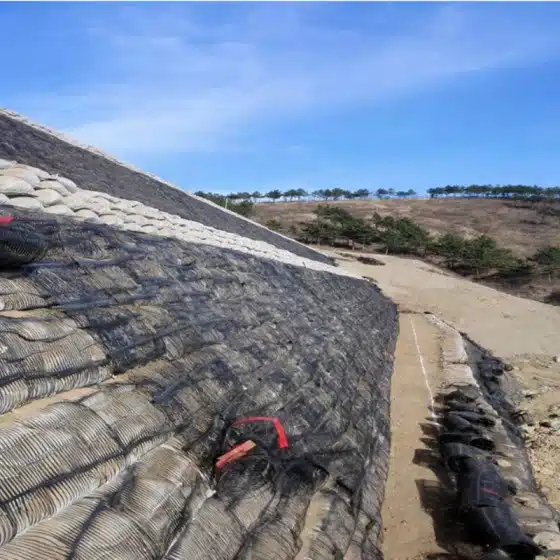
How to Use Geogrid in Retaining Walls & Hillsides
A. Geogrid fabric retaining wall (MSE):
- Leveling pad & face
- Construct footing/leveling pad; set blocks/panels true to line and grade.
- Layering geogrid
- At specified courses, pull polyester geogrid from the wall face into the backfill. Keep it tensioned and flat.
- Embedment length (Lr): follow design (commonly 0.6–0.8× wall height or as per calcs). Avoid shortcuts.
- Backfill & compact
- Use well-drained granular backfill. Compact to spec in thin lifts, staying 3–6 ft (1–2 m) behind the face to avoid bulging; then carefully compact near the face.
- Drainage
- Add chimney/blanket drains and weeps. Keep fines out of the face.
B. Geogrid slope stabilization / geogrid for hillside:
- Surface prep
- Grade, remove sloughing soil, install toe key if needed.
- Grid placement
- Place uniaxial or biaxial PET layers at the design spacing (e.g., 0.6–3.0 m vertical). Anchor at the crest with trench or pins.
- Backfill & wrap
- Place reinforced soil lifts; lightly tension geogrid; compact to density. Wrap at face or integrate with facing (ECM, shotcrete, blocks, or vegetated facings).
- Erosion control
- Add surface matting, hydroseed, and drainage breaks to manage runoff.

Geogrid Rolls: Selection, Handling & QA
- Roll width & length: choose widths that minimize overlaps and waste on your platform or wall geometry.
- Strength class: specify design tensile strength at 2% and 5% strain and the long-term design strength (LTDS) after reduction factors.
- Aperture & coating: match to aggregate and soil chemistry.
- Handling: store rolls off the ground; keep packaging intact; unroll with a bar or spreader to keep alignment straight.
- QA/QC: check mill certs for tensile, junction efficiency, and coating mass; confirm roll labels match submittals.
Estimating the Cost of Geogrid & Quantities
Takeoff method (quick):
- Driveways/bases: Area ÷ roll coverage (account for overlaps, waste) = number of geogrid rolls.
- Walls/slopes: Reinforced area ÷ (roll width × effective layer spacing) = rolls.
Cost of geogrid—what drives it:
- Polymer system (PET vs PP/HDPE), polyester geogrid coating type, strength class, roll width/length, and certification requirements
- Volume breaks, project location, Incoterms, and freight (rolls are bulky)
Ways to save without sacrificing performance:
- Optimize layer spacing and embedment via design, not blanket “one-size” assumptions
- Use biaxial in bases and uniaxial in walls/slopes where each is most efficient
- Coordinate aperture with locally available aggregate to avoid special orders
Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
- Tracking equipment directly on exposed geogrid (push off with aggregate first)
- Insufficient overlaps on soft subgrades
- Poor drainage behind walls or on slopes leading to hydrostatic pressure
- Wrong aperture for the selected base course—no interlock, no stiffening
- Skipping compaction control—strength comes from grid + properly compacted soil
When You Need a Proven Supply Partner
MJY Geosynthetics Manufacturer has been dedicated to producing high-quality geosynthetic materials for 15 years and is a recognized leader in the industry. If you are interested in finding a reliable one-stop geosynthetics supplier for your project or business, please visit our website for more information。
Conclusion
Use geogrid where soil needs tensile help: stiffen bases for geogrid for driveway projects, reinforce soil in geogrid slope stabilization on a hillside, and build economical geogrid fabric retaining wall systems. Select the right polyester geogrid, size your geogrid roll inventory correctly, control overlaps and compaction, and manage water. Do that, and you’ll deliver longer service life, less rutting, and cleaner bids—while keeping the cost of geogrid firmly under control.





